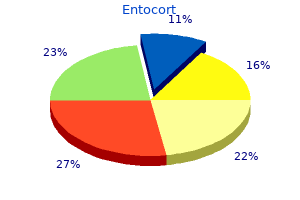
Mark A. Graber, MD
- Professor
- Departments of Family Medicine and Emergency Medicine
- Roy J. and Lucille A. Carver College of Medicine
- University of Iowa
- Iowa City, Iowa
Make sure you look at the fundus by retroversion of the endoscope looking towards the cardia You should see a small pool of gastric juice in the where you will see the black tube of the instrument posterior part of the body of the stomach: suck this out and coming through allergy testing blood or skin purchase 100 mcg entocort free shipping. You then will notice a ridge ahead be able to see the cardia close up; look again at the (the incisura allergy vacuum cleaner buy entocort cheap, or angulus) above which is a view of the oesophagus and pharynx as you come out allergy treatment prescription order entocort 200mcg. It will tend to slip past against the procedure: There is either a perforation or a myocardial bulb of the duodenum allergy shots pain order entocort without prescription, and so need withdrawing a little: infarction peanut allergy symptoms 1 year old entocort 100 mcg cheap. If you find yourself seeing the instrument coming through the cardia allergy symptoms dry throat order cheapest entocort, he will start belching. Withdraw the endoscope tip and turn it towards the left, and advance again provided you can see where you are going! Remember there may be gross pathology to confuse you: achalasia, large diverticulum, duodenal Fig. However, there is a risk of regurgitation and the correct width, and long enough and thread it through aspiration, so do not persist and try again after nasogastric the biopsy channel. Beware: food particles and thick candida can it may not pass if the endoscope is very retroverted or of block the endoscope channels and damage them. Take specimens under direct vision If you can’t withdraw the endoscope, check that the by instructing an assistant how and when to open and close viewing control ratchet is free and manipulate them so the the forceps, and shake them directly into a container with instrument is straight. However, if you are not asymmetrical with exuberant abnormal mucosa and raised experienced you may need longer than diazepam alone ulcer edges but a gastric carcinoma may infiltrate under will allow; add ketamine or pethidine. With the tip of the guide abnormality except excessive food residue which may look wire nicely beyond the stricture, gently withdraw the like candidiasis. When it becomes visible at the mouth, ask your clinical significance and biopsies may be more helpful. Erosions start as or of stepped graduation (Celestin type); pass them over umbilicated polyps and then develop into smooth-margin the guide wire past the stricture and then withdraw them. Biopsy all gastric lesions for a correct the dilator, introduce the endoscope again to check the diagnosis. You can highlight lesions more easily by spraying the surface with a little methylene blue or Such dilation will unfortunately not help in achalasia ordinary ink, with an injection device passed through the (30. Make sure you have bleeding or evidence of recent bleeding; the Forrest measured the position of the malignant stricture. If you have self-dilating stents, these are a big When you see an actively bleeding vessel in a duodenal improvement on the basic fixed tube described. The problem is that you may not actually see the bleeding point if the stomach is full of blood, so make sure you have passed a nasogastric tube beforehand and sucked it out. If you have the more sophisticated equipment, you may be able to clip a bleeding vessel. Physical cleaning of the instrument is essential: disinfectant may solidify mucus and actually make its Fig. Clean the tip To prevent bleeding, it is best to have a plastic sleeve, with a toothbrush. Do not wet the control head of the specially made for the purpose from suitable tubing, with instrument. Pass the cleaning brush through the and then rotate the plastic so that the tube presses against channel, and clean the bristles after they emerge from the the varix and stops the bleeding. You may need to injections till you have satisfactorily dealt with all the repeat this several times. If bleeding the biopsy port and aspirate disinfect into the channel, persists, sedate the patient and leave in the overtube for leaving it there for 2mins. Connect a bottle of disinfectant in place of the water bottle and flush this through the air/water channel, and then clean it with water and air. Remove the washing adaptor, suck hydrogen peroxide and then 30% alcohol through the biopsy channel, and then dry the instrument in air. Wipe the tip and outside of the instrument with a gauze soaked in 30% alcohol and leave it to dry. Remove the air/water and suction Using an valves; clean these and lubricate them with silicone jelly endoscope sleeve. Remember most foreign bodies in the Produce a regular form (13-10) with patient details, stomach will pass normally. An overtube, as used for varix instructions, consent, indications for the procedure, injection, is useful to protect the oesophagus and pharynx; and findings. Make sure you fill these correctly for each pass it beyond the cardia and then grasp the foreign body patient. If he survives, there is a 50% chance of needing further peptic ulcer medical treatment, but <10% will require further major surgery. Although the standard treatment is an urgent laparotomy to close the hole in the duodenum or stomach, and to wash out the peritoneal cavity, there are some indications for treating non-operatively, as described below. This is less demanding technically, but it needs careful clinical observation, and you will need good judgement to know: (1) when you have made a wrong diagnosis, and (2),when non-operative treatment is failing, so that you need to operate. Closing the perforation is not difficult, but be Make sure you fill in all the relevant details: pictograms are best at sure to wash out the peritoneum when it has been demonstrating what you’ve seen. The patient can often tell late in a perforation), shock (when generalized rigidity is you the exact moment the pain began; it is constant, the result of appendicitis, shock is unusual), and >1l of it spreads across the entire upper abdomen and later all stomach aspirate. Then, at about 6hrs, signs of diffuse peritonitis develop, accompanied by abdominal distension and absent bowel sounds. Continue to keep him nil orally on nasogastric diaphragm and the liver or stomach. If he cannot sit or drainage for 4-5days, until the abdomen is no longer stand, take a film semi-erect propped up in bed: this is tender and rigid, and the bowel sounds return. Much fluid will be lost into the peritoneal cavity, so correct at least ½ of the fluid loss before you operate. If >12hrs have elapsed since the (2);The absence of really good nursing by day and night. Operate soon, but not (3);The seriously ill patient, with a short history, whose before proper resuscitation. Unless there has been only hope is vigorous resuscitation and an urgent bleeding (rare), do not transfuse blood. The fluid may time to act, pass as wide a radio-opaque nasogastric tube be odourless and colourless with yellowish flecks, as he will tolerate. Look for If you see patches of fat necrosis, this is due to acute subdiaphragmatic gas to confirm the diagnosis. Look in the right Back in the ward, ask a nurse to aspirate the stomach every paracolic gutter and draw the stomach and transverse 30mins initially, making sure the tube is cleared by colon downwards: you may see flecks of fibrin, and injection of 5ml of air before aspiration. If necessary, get the If this is normal, examine the gallbladder, pancreas and help of a second assistant. Suck away any fluid, looking carefully to see where it is To close the perforation, place 0 or 2/0 long-acting coming from. Search for a small (1-10mm or more) absorbable sutures on an atraumatic needle superior and circular hole on the anterior surface of the duodenum, inferior to the hole (13-11B); then tie these sutures over an looking as if it has just been drilled out. The tissues omental fold onto the stomach or duodenum thus covering around it will be oedematous, thickened, scarred, and the hole (13-11C). Do not try to bring the ulcer edges together: if the sutures If the duodenum is normal, look at the stomach, cut out, the hole will be much larger than before. If the hole is small, there may With a large hole, you can use the omentum actually to be more to feel than to see. Sometimes, a gastric ulcer is plug it, but this does not safely close perforations >2cm sealed off by adhesions to the liver. Check if the hole is sealed by gastric ulcer may be malignant: take a biopsy if this does passing some dye. An ulcer high up Tip a litre of warm fluid into the peritoneal cavity, posteriorly may be difficult to find. Breathing will then be easier, chest complications less likely, and any exudate will gravitate downwards. Chest physiotherapy is vital if he is asthmatic, a smoker, immune-compromised, elderly, or if there is widespread soiling in the abdomen. Treat him with antibiotics for helicobacter as >80% of perforated ulcer patients have it. Start an H2-blocker or proton-pump inhibitor immediately (dilute crushed tablets with water and introduce this via the nasogastric tube, and then clamp it for 1hr) and continue oral treatment for 6wks. If this is difficult, or it is leaking into the peritoneal cavity, cut around it, and leave its base fixed. If the ulcer is huge, leaving only a small part of A, retract the stomach and expose a perforation on the anterior of duodenum normal, closing it will be impossible or result the duodenum. B, place interrupted stay sutures of 0 or 2/0 silk or in stenosis; mobilize the duodenum by dividing the absorbable on an atraumatic needle adjacent to (but not through) the peritoneal attachment along its convexity (the Kocher perforation, C, in order to pull a fold of omentum over the hole. Your task is to: stab incisions in the abdominal wall, label them clearly, (1) resuscitate the patient, and secure them firmly. If this comes out through the stomach Foley drain, wait Try to make the diagnosis epidemiologically and and try again later. Eventually the area of ulceration will clinically, especially if you do not have a fibre-optic close by scarring. The important distinction is whether or not bleeding is If there is concurrent bleeding, there is probably a large from gastro-oesophageal varices, because you will not circular or ‘kissing’ ulcer: try to undersew the bleeding want to operate on these, whereas you may need to operate vessel first. A large spleen is a most incision including the perforation and then try closing it useful sign. If this is impossible, use an omental plug, with a However, even the best surgical centres cannot find a retrograde tube duodenostomy and feeding jejunostomy as cause for the bleeding in about 10% of cases. There is at least a 25% If an ‘hourglass stomach’ perforates, it is from stricture chance that the patient has a peptic ulcer and no due to acid ingestion (13. Note sweating, restlessness, mental If there is a pergastric abscess in Morison’s pouch or the slowing and oliguria. Falling blood pressure is a sign that lesser sac, drain it by a separate incision in the flank. Examine for epigastric tenderness, and rectally to make sure that a history of If pyrexia ensues in the 2nd week post-op, suspect there black tarry stools is correct. If the blood is bright red, and is a subphrenic abscess or other localized collection of pus the patient is not shocked, the bleeding does not come from (10. If you continue to obtain much gastric aspirate, there is If there is vomiting blood and you have no reason to probably a pyloric stenosis aggravated by the duodenal suspect severe oesophageal varices, pass a nasogastric tube closure. If it continues for >10days, perform a and monitor the amount of bleeding into the stomach by gastrojejunostomy (13. Ascites is common in cirrhosis, less common and tract, but in certain parts bleeding varices as the result of often not marked in periportal fibrosis, and very portal hypertension are more common. Spider naevi, and Other causes of bleeding include stress ulcers, palmar erythema are often not seen. The patient may be haemorrhagic gastritis, uraemia, gastric carcinoma, drowsy or in coma from hepatic encephalopathy (made a tear in the lower oesophagus following a forceful vomit worse by the digestion of the blood in the bowel). Liver function tests are abnormal in cirrhosis, but often normal in portal fibrosis. Melaena alone is not as serious as haematemesis, Decide if the blood loss has been mild, moderate, but beware of continuing melaena and unaltered blood in or severe. Small melaena stools or small bloody vomits or chlorpromazine 25mg, or use ketamine. The resting pulse may only be 90/min, but the least exertion may send it up to ≥120/min. If you have a colloid plasma expander, infuse 1-2l (After 3days, however, re-bleeding is unlikely. A rapid fall in remember then that your threshold for operative Hb 8hrs after an initial bleed indicates continued bleeding. If you think gastro-oesophageal varices are unlikely, Remember Moshe Schein’s dictum: pass a large nasogastric tube. This will tell you if bleeding “When the blood is fresh and pink, and the patient is old, is continuing, and whether the blood is fresh or altered. Then run into the stomach 200ml ice-cold saline you can relax and put your knife on hold. Common Sense Abdominal Emergency containing 8mg noradrenaline and leave it for 30mins; Surgery, Springer 2nd ed 2005 p. Measure and chart the pulse, the blood pressure, and the Later, if possible, perform endoscopy, or a barium meal. A rising pulse or a sustained tachycardia are more important than isolated readings. For the high risk patient, (the indicators are: Monitor the urine output, and, if possible, the central haematemesis as well as melaena, pallor, loss of venous pressure if the patient is very ill. Ideally every patient with an tachycardia, pallor, restlessness, bright red fluid aspirated upper gastro-intestinal haemorrhage should have an through the nasogastric tube, and the rapid fall in Hb or its endoscopy. Unless you have good suction, however, failure to rise in spite of transfusion (a useful sign). Look for adherent blood Monitor glucose levels in liver disease, and liver function clots in an ulcer, a visible vessel ‘standing up’ in the ulcer tests if possible. This is most useful, if you can do it, of sclerotherapy for varices and injection or clipping of but it will be almost impossible during heavy active vessels in bleeding ulcers (13. Once it has settled, it will allow you to inject Remember Helicobacter pylori is almost always present gastro-oesophageal varices (13-9), or inject around a where ulcers bleed, so use antibiotics (13. At this point you will the bleeding point may be difficult to find, and when you have to decide whether or not to operate in the hope of have found it, blood may obscure it, so that controlling it saving life.
Depots of crystalline suspensions on the inhibitory effect which one organism exerts on another allergy shots utah order 100 mcg entocort. Other antimicrobial most cocci other than penicillinase-producing staphylo agents are effective against spirochaetes allergy shots or sublingual order entocort with mastercard, rickettsiae allergy shots pills discount entocort 100 mcg with amex, fungi and cocci allergy urticaria buy online entocort, Neisseria and partly Escherichia coli allergy symptoms yearly discount 100 mcg entocort amex. In general allergy testing does it hurt buy entocort now, effectivity against gram-positive organ isms is seen with penicillin G, erythromycin, oxacillin and Their intraocular penetration is good. Carbenicillin vancomycin, while neomycin, polymyxin B, azlocillin and sodium, ticarcillin and azlocillin are given parenterally and streptomycin are largely effective against gram-negative act against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The ‘broad-spectrum’ antibiotics—gentamicin, Penicillins show a synergistic action with antibiotics amikacin, ampicillin, cephalosporin, tobramycin, chloram of the aminoglycoside group. In deep-seated infammations phenicol, tetracycline, fuoroquinolones and others—are of the orbit or lids, they are administered parenterally. Cloxacillin and fucloxacillin: these penicillins are not Most of the currently available antibiotics are extremely affected by staphylococcal penicillinase and are therefore effective for conjunctival and corneal infections, and should used for treating staphylococcal infections which are resis be prescribed to be used every 1–2 hours for a few days and tant to other penicillins. If a fuoroquinolone or aminogly against penicillin-resistant staphylococci as cloxacillin, but coside drug does not show clinical effcacy, the drug should levels of fucloxacillin in the blood after oral administration be switched or a drug from another group added. This is because fucloxacillin is better absorbed from medications, their dosages and routes of administration. Serum levels following intramuscular or intra Penicillins venous injections of fucloxacillin are also higher than those All penicillins have a bactericidal effect, but have a short of cloxacillin. Differences in antibacterial activity, absorption Carbenicillin is resistant to the penicillinase produced and resistance to penicillinase depend on alteration of the by some strains of Proteus, Pseudomonas and coliform side-chains attached to the amino group. Most of them have a rather narrow antibacterial should be used for organisms which are resistant to benzyl spectrum, being chiefy confned to cocci and gram-positive penicillin but do not produce penicillinase. They diffuse readily into tissue fuids but not into Amoxycillin: this penicillin has an antibacterial activity the eye. When given systemically some have to be injected identical to that of ampicillin but its main advantage is intramuscularly because they are destroyed by the acidic that it is well absorbed after oral administration, producing gastric juice, others can be given by mouth. As patients are serum levels about twice as high as those after an equivalent liable to develop hypersensitivity to penicillin, it is wise to dose of oral ampicillin. Food in the stomach has little effect enquire about this before starting a course of treatment. The adult Immediate reactions such as urticaria and anaphylactic dose is 250–500 mg every 8 hours. Penicillins effective against coccal infections and drops effectively penetrate the vitreous. Oral gatifoxacin has gram-positive bacilli: Benzyl penicillin is not acidstable been shown to have extremely high levels in the vitreous. Penicillinase-resistant penicillins consist of cloxacillin these drugs have a structure and mode of action similar to sodium and flucloxacillin sodium. They are relatively resistant in their activity against penicillin-resistant staphylococci. Broad-spectrum penicillins such as ampicillin and penicillin may develop an allergy. When cephalosporins are amoxycillin are absorbed well orally and can also be used extensively, strains of staphylococci resistant to cloxa administered parenterally. The main adverse effect of of activity against many gram-negative organisms and gram cephalosporins is nephrotoxicity. All these agents are toxic to the eighth nerve and the hazolin and cephalexin, were highly effective against kidney, and interfere with neuromuscular conduction, causing gram-positive cocci, but moderately so for some gram serious paralysis in patients with myasthenia gravis or those negative enterobacilli. Intravitreal injec sporins, such as cefuroxime and cefaclor, had a wider tions are retinotoxic and may cause macular infarction. Some of the third-generation Streptomycin: this bactericidal drug is used in the cephalosporins. Thus, the drug Cephazolin is suitable for either intramuscular or intra should be used only after confrmation of in vitro suscepti venous administration. Cephradine can be given orally, intramuscularly or Soframycin is highly effective against gram-positive intravenously. Gentamicin: this drug may be used parenterally for the Ceftazidime acts against many gram-positive and gram treatment of serious infections by gram-positive and gram negative organisms, especially Pseudomonas. As the margin between toxicity and eff dose of 1–2 g intramuscularly or intravenously is given every cacy is narrow, it should be reserved for infections resistant to 8–12 hours. Because it is nephrotoxic and ototoxic and Cefuroxime and cefotaxime are available only as inject secreted through the kidneys, the dose must be decreased in able preparations. Gentamicin is effective against an exceptionally wide range of bacteria Aminoglycosides which includes penicillin-resistant strains of staphylococci this group includes streptomycin, soframycin, neomycin, and Ps. Pseudomonas strains show an increasing gentamicin, sisomycin, netilmycin, tobramycin and amikacin, incidence of resistance to gentamicin, therefore amikacin is Chapter | 13 Ocular Therapeutics 151 recommended for treating intraocular infections. Bactericidal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylo concentrations are found in the aqueous following topical coccus epidermidis. As it may occasionally cause conjunctival necrosis, the It is the drug of choice in endophthalmitis together sub-Tenon route is recommended. It is toxic if used topically or Neomycin: this has similar properties to gentamicin subconjunctivally. It can be used topically, especially in combination with another antibiotic as eye Fluoroquinolones drops or ointment, but often causes contact allergy. These bactericidal drugs are derivatives of nalidixic acid and Sisomycin and netilmycin are similar to gentamicin, but have a broad spectrum of activity. Fortifed drops enhance treats a broad range of ocular pathogens, in conjunctivitis – bioavailability and it can also be given sub-conjunctivally Haemophilus infuenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphy or intravitreally. Because these drugs get deposited in the growing but is more retinotoxic than ceftazidime. For the treatment cartilage, they are not routinely recommended for treating of endophthalmitis, 0. Other Antibiotics Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol: this bacteriostatic antibiotic is effective Tetracyclines such as tetracycline, chlortetracycline and against bacteria, spirochaetes, rickettsiae, chlamydiae and oxytetracycline are broad-spectrum antibiotics with consid mycoplasmas. The molecule is small and lipid soluble so erable bacteriostatic action against both gram-positive and that on systemic administration it enters the eye in thera gram-negative organisms as well as some fungi, rickettsiae peutic concentrations. However, its effects on intraocular and the chlamydiae; the last group includes the infective infammations are usually not dramatic. Many bacteria have now developed spectrum for superfcial ocular infections and does not resistance to these drugs. Of all topical lar tissues either from the conjunctival sac or after systemic antibiotics, it is the least toxic to the corneal epithelium. They are administered essentially Topical administration may rarely lead to blood dyscrasias. They are often used topically in combination with orally in acne rosacea and chronic staphylococcal infection neomycin, bacitracin and gramicidin for superfcial eye of the lids and conjunctiva. They are useful against extra or intraocular provide better aqueous concentrations. Sulphonamides Macrolide and Lincomycin Groups this group of drugs has a bacteriostatic effect on most Erythromycin, azithromycin, lincomycin and clindamycin are gram-positive bacteria and chlamydia. They are used in relatively narrow-spectrum bacteriostatic agents used for the treatment of toxoplasmosis in combination with pyri treating gram-positive infections and those due to Chlamydia methamine or trimethoprim. Antiviral Agents Azithromycin is long acting and is used as a single stat dose of 500–1500 mg (20–30 mg/kg) in the treatment of Antiviral drugs used to treat herpesvirus infections are trachoma, toxoplasmosis and Lyme disease. Eighty-fve per ocular implant containing 5–6 mg of ganciclovir can be cent of initial dendritic ulcers treated with 0. Commonly seen Other Antiviral Agents toxic reactions are superfcial punctuate keratitis, follicular Foscarnet inhibits the replication of all human herpes and conjunctivitis and punctal occlusion. This drug is soluble and more effective than others Zidovudine inhibits the virus-induced reverse transcrip in the prevention of complications produced by corticoste tase which is essential for virus replication in the infective roids. Antifungal Agents Acyclovir is a selective, virustatic drug, which is acti vated largely in virus-infected cells. It is of proven value Polyene Antibiotics in the treatment of acute cases of the common herpesvirus Amphotericin B is the most effective antibiotic in the treat infections such as herpes simplex keratitis and herpes zos ment of systemic fungal infections. It is used as 3% ointment fve times a day till all activity of keratomycosis, metastatic and exogenous endophthalmi subsides and is less toxic than the other antiviral drugs. It can be given in a dose of 5–10 mg intravitreally herpes simplex iridocyclitis, and acute herpes zoster and incremental doses are given i. It is not absorbed by mouth dose of 800 mg fve times a day for 7–10 days is adminis and is applied topically as a suspension (1 00 000 units/g). It is also effective against the hour and then tapered off as the infection subsides. An oral maintenance dose of 1 g Acyclovir 3% ointment is given thrice daily with meals. They are less toxic than the polyenes and are also effective against bacteria and Corticosteroids are very effective for treating infammations Acanthamoeba. Unfortunately, they Topically, Clotrimazole 1% and Econazole1 2% are also produce substantial local and systemic side effects. Mechanism of action: They act by suppressing the Miconazole is effective against yeast and flamentous formation of arachidonic acid and other infammatory me fungi and is used topically as 1% drops hourly or as a 2% diators by the induction of phospholipase A2 inhibitory ointment given 6 hourly. In cases of fungal endophthalmi of corticosteroids may lead to the formation of posterior tis, adnexal or severe corneal infections, it can be given subcapsular opacities in the lens and is known to cause glau orally in a dose of 200–800 mg daily for 7 days and up to coma in genetically susceptible persons. Its the general clinical effect of these drugs is a temporary adverse effects include liver toxicity. Subconjunctival and blockage of the exudative phases of infammation and an intravitreal injections may also be given. Oral absorption is good, with effective Phospholipids from damaged cell membranes corneal and anterior chamber concentrations at 100–200 mg 6 hourly. Glucocorticoids Phospholipase A2 X Itraconazole: this drug is similar to ketoconazole and is well tolerated orally in a dose of 100–400 mg daily. Ketoconazole has the highest incidence of adverse effects, which limits its usefulness. Itraconazole and voriconazole have activity against Aspergillus, which normally must be treated with amphotericin B. In acute infammations, capillary per meability is decreased and cellular exudation reduced, Steroids Used in Common Anti-infammatory while in the stage of healing, the formation of granulation Ophthalmology Dosage Potency tissue, new vessels and fbrosis is diminished. Therefore, it follows Prednisolone acetate/ 1% 4 that corticosteroids primarily control acute disease and are phosphate completely ineffective in the removal of structural damage Betamethasone 0. Methylprednisolone 5 A solution of 1% prednisolone acetate has the greatest anti-infammatory action, followed by 0. They thus may play Loteprednol is a ‘soft’ steroid has no effect on the intraocu a role in regulating edema. Triamcinolone acetonide in lar pressure or systemic side effects as it binds to the gluco an intravitreal dose of 1/2/4 mg has been evaluated in the corticoid receptor and the remainder is rapidly metabolized treatment of retinal diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, to an inactive metabolite in the eye (Table 13. Corticoste exudative age related macular degeneration, cystoid macu roids are used as drops every 6 hours or more frequently, lar edema, venous occlusion, Eales’ disease etc. Frequent instillation of drops is as effective as subcon High doses of methylprednisolone intravenously are given junctival injections. Periocular injections of corticosteroids, in ‘pulses’ to treat optic neuropathies. These drugs are now replacing steroids in less severe Steroids can down-regulate infammatory stimuli by or more chronic infammations. They act by inhibiting modulating the response of the vascular endothelial growth the cyclooxygenase pathway for prostaglandin formation Chapter | 13 Ocular Therapeutics 155 (Flowchart 13. Systemic supplementation is Cycloplegics and Mydriatics required for diseases involving the retina and uvea. The latter allows zonular along with mydriatic–cycloplegics are used for preventing laxity and a consequent thickening and forward movement intraoperative miosis, and 6 hourly in the management of of the lens necessary for the visualization of near objects, postoperative infammation. Atropine 1% eye ointment is used for refraction and fundus examina Antihistamines tion in children, especially those with darkly pigmented Antihistamines show a competitive antagonism to histamine irises and those less than 5 years of age. They ing hence ointment is preferred over drops in young chil are used for vernal keratoconjunctivitis, giant papillary dren. Atropine 1% drops or ointment may also be used as conjunctivitis and other forms of allergic conjunctivitis. H1 receptor antagonists are emedastine when atropine is used for prolonged periods. Homatropine used four times a day, and azelastine used once or twice a 2% drops are less potent and used in the treatment of uveitis day. In severe cases, loratadine, cetrizine and astemizole can and for refraction in children. Cyclopentolate 1% drops three times 5 minutes apart are used for refraction and fundus exami Mast Cell Stabilizers nation in children. A 2% ointment can be Side effects of cycloplegics are blurred vision and photo used at night. In patients above 60 years of age having Ketotifen drops are instilled thrice a day. This drug is hypermetropia and a shallow anterior chamber, mydriasis also a mast cell stabilizer but has the advantage of a quicker may precipitate acute angle-closure glaucoma. Olopatadine has both a mast cell stabilizing effect and these dilate the pupil and are used prior to fundus examina an antihistaminic action. Phenylephrine 5–10%, a selec on the trabecular meshwork increasing the size of the pores. Side effects include In eyes having a narrow angle recess or angle-closure glau stinging on application, and a rise of blood pressure in coma, constriction of the pupil pulls the peripheral iris away predisposed individuals. Its therapeutic effect begins in half an hour, At present, the treatment of glaucoma is aimed at lowering with a peak action at 2 hours.
Chapter 160: corneal changes are accompanied by a gross diminution of Topographic analysis in keratorefractive surgery allergy blood test order discount entocort. Quantifcation of the corneal sensation is possi described as ‘mutton fat’ allergy treatment 5 shaving buy entocort us, and are seen in granulomatous ble to some degree by the use of a corneal aesthesiometer uveitis allergy shots side effects fatigue buy entocort with american express, whereas fne keratic precipitates are present in in which a single horse hair of varying length is used in Fuchs cyclitis and herpes zoster uveitis allergy medicine and decongestant entocort 200mcg lowest price. The longest length which induces blinking is a measure of the threshold of corneal the Corneal Endothelium sensitivity allergy forecast washington dc buy generic entocort 200mcg. The corneal endothelium can be examined cursorily by the specular examination technique on the slit-lamp allergy testing no needles purchase online entocort. Staining Objective examination with the specular microscope To determine the state of the corneal epithelium, the tech (Fig. Three dyes through a slit aperture into a system of mirrors which are usually employed. Fluorescein is the most useful to direct the light into the cornea through an objective lens delineate areas denuded of epithelium (abrasions, multiple and its attached ‘dipping cone’. The dipping cone lens erosions, ulcers) which stain a brilliant yellowish green, has a fat surface extension on the water immersion when examined with cobalt blue light. Rose Bengal stains objective that applanates the cornea as in applanation diseased and devitalized cells red (as in superfcial punctate tonometry. Alcian blue dye stains the mucus selectively and the dipping cone to focus the image of the cornea for delineates excess mucus produced when there is a def different thicknesses. The light is refected from the endothe lium and back through the objective lens eye-pieces at Opacities of the Cornea 2003 magnifcation and may be observed through an Opacities of the cornea may be so faint that they require eye-piece, camera or monitor. With age, there is a signifcant decrease in cell particular importance is the detection of the minute epithe density and variation in cell size (pleomorphism and poly lial or subepithelial lesions of superfcial punctate keratitis megathism) of the endothelial cells. The specular micro and keratic precipitates, small accumulations of infamma scope enables the surgeon to perform a cell count before tory cells derived from the uvea which adhere to the mid using material for corneal grafting. The presence of keratic amount of endothelial cell loss seen after any intraocular precipitates indicates infammation in the uvea. Large, waxy keratic precipitates are also complex optical principles, this acquires multiple images Chapter | 11 Examination of the Anterior Segment 119 Depth 1 the anterior chamber is shallow in the very young and in old 2 age. The iris is viewed through the cornea, which is a strongly 3 refracting convex surface. The effect of this is to magnify the 10 4 iris and pupil, and to make them appear closer than they re 5 6 ally are. The depth of the anterior chamber is estimated as the 7 distance between the posterior surface of the cornea and the anterior surface of the lens. The depth of the anterior cham 9 8 ber can be clinically evaluated by focussing a beam of light A on the temporal limbus, parallel to the surface of the iris. In a normal or deep anterior chamber the beam will pass through directly, illuminating the opposite limbus (Fig. In eyes with a shallow anterior chamber, the anterior place ment or bowing forward of the iris obstructs the light and a shadow is observed on the medial half of the iris and limbus (Fig. A comparison of the depth of the peripheral an terior chamber to the peripheral corneal thickness is used to determine the degree of shallowness of the anterior chamber in the van Herrick method. An optical section of the peripheral cornea and anterior chamber is made on the slit-lamp with the illumination and viewing arms at 60° to each other, and the viewing arm perpendicular to the cornea, using a magnifca B tion of 15. Copyright by the Ophthalmic Publishing can be measured optically by the pachymetry attachment of a Co. B from Jay H Krachmer, Mark J the anterior chamber is usually shallow in angle-closure Mannis, Edward J Holland. It is frequently unequal in depth in different Ann Benetz, Richard Yee, Maria Bidrsos, eds. The iris is bowed forwards (iris bombé) it is funnel-shaped, the images are magnifed and show endothelial and epithelial centre being deep, the periphery shallow. Analysis of these images provides of the lens causes it to be deeper on one side than on the other. In infammatory conditions of the uveal tract where the permeability of the vessels is increased, the aqueous may contain particles of protein or foating cells. The curvature of the anterior surface of the cornea can be measured by a keratometer and the corneal thickness by an Contents optical pachymeter on a slit-lamp or an ultrasonic pachym eter. The topography of anterior and posterior surfaces of Protein transudation from the iris or ciliary vessels pro the cornea are assessed by a digital analysis of over a thou duces an opalescence of the aqueous, an aqueous fare sand points on the cornea (see Fig. The aqueous cells are recorded as: Hyphaema: A similar collection of blood may occur after contusions or spontaneously (hyphaema). Micro-flariae l trace if 1–5 are present may be observed in the anterior chamber in eyes with l 11 if 5–10 onchocerciasis. A dull iris with an ill-defned pattern or ‘muddiness of Very large, non-reactive pupils will suggest that a myd the iris’ suggests atrophy from iridocyclitis and sectoral riatic has been used, perhaps inadvertently, as when a pa patches of atrophy suggest an acute angle-closure glaucoma tient has been using an ointment containing atropine, and or herpes zoster. The Tremulousness of the iris or iridodonesis is seen when pupils are usually immobile, and the patient complains of the eyes are moved rapidly if this tissue is not properly sup dimness of vision, especially for near work. This occurs in absence, shrinkage, or the pupils are also large and immobile in bilateral le subluxation of the lens, and is best appreciated in a dark sions affecting the retina and optic nerve causing blindness room with oblique illumination, on asking the patient to (see Fig. Bilateral dilated pupils, in bilateral in Down syndrome and pedunculated nodules (Lisch) in blindness, can be distinguished from a bilateral efferent neurofbromatosis. Flat nodules at the pupillary margin pupillary defect, pupilloplegia, by eliciting the near refex. It is equally important to the position of the iris must be examined next, espe remember that the presence of a direct reaction to light does cially the plane in which it lies. Special attention should be not eliminate the possibility of the patient actually being paid to any adhesions or synechiae, anterior to the cornea blind due to a central lesion affecting the visual pathways or posterior to the lens capsule. The size of the pupil is determined by the afferent and effer Dilated and immobile pupils also result from third nerve ent pathways for pupillary light refexes, and the function of palsies (absolute paralysis of the pupil); if the paralysis the sphincter and dilator pupillae muscles. Dilatation of the also affects the third nerve fbres to the ciliary muscle, ac pupils with retained mobility is found sometimes in myopia commodation is also paralysed (ophthalmoplegia interna). This results in lesions affecting the third nerve nucleus, Conversely, the pupils are small in babies and in old people. This may be due to conditions hand and watch the pupil, noting if its constriction to light such as swollen lymph nodes in the neck, apical pneumo is well maintained. Replace this hand and remove the other, nia, apical pleurisy, cervical rib and thoracic aneurysm. Most of the conditions causing an process is repeated while observing the other pupil. When all sympathetic function on to an absence of natural light or diffuse illumination. More one side is lost, resulting in miosis, a narrowed palpebral over, when the reaction to light is feeble and the pupils are fssure and slight enophthalmos (due to loss of tone already small, it is diffcult to be certain of the results in of Muller muscle), sometimes associated with unilateral bright, diffuse daylight. In such cases the examination absence of sweating, the condition is called the Horner should be carried out in a dark room and light concentrated syndrome. By slight lateral movements the focus of light sluggish pupil with ‘muddiness’ of the iris is associated can be moved on or off the pupil, the pupillary movements with an active iritis. Still fner observations can be iritis with posterior synechiae, and should be investigated made with the slit-lamp, when the microscope is focussed with a mydriatic such as cyclopentolate to ascertain if the on the papillary margin and the beam is abruptly switched pupil dilates regularly. If there is no irritation of the third nerves, arousing suspicion of a central movement in these conditions it may be concluded that the nervous disease in their vicinity. The light is focused frst on the large, immobile and oval, with the long axis vertical. The best source of illumination for this purpose is the focal beam of Pupillary Refexes the slit-lamp reduced to a spot. If the reaction is present During routine examination of the eyes, the pupils should the pupil will react briskly when one half of the retina is be examined at an early stage, before any mydriatic is em illuminated, but very slightly when the other half is illumi ployed. This is so because it is impossible to prevent diffusion and is best carried out with low background illumination of light onto the sensitive half of the retina, so the test is using a bright focused light with the patient looking into the rarely unequivocal. After 2–3 seconds, the should be kept in mind: light is rapidly transferred to the opposite pupil. This swinging to-and-fro of the light is repeated several times l Illumination in the examination room should be low while observing the response of the pupil to which the light l the patient should look into the distance, and is transferred (Fig. The patient is asked to look consensual response has the same magnitude as a direct into the distance to prevent accommodative constriction of response. Note the size, shape and contour of each pupil, input from that side is less than that from the normal side. In that case when the light is transferred to the diseased eye these refexes are: (i) constriction of the pupil to direct both pupils will dilate, and on swinging back to the normal or consensually presented light and (ii) accommodation— side both the pupils will constrict. This is referred to as light near determined by asking the patient to look to the far end dissociation. While he does so an accommodation target the tonic pupil (of Adie) somewhat resembles the is suddenly held up vertically at about 15 cm from the Argyll Robertson pupil; it is of unknown aetiology, not patient’s nose and he is told to look at it. The movement of associated with syphilis, occurs usually in young women, is the pupils is studied while he converges. This When properly conducted, the above method provides pupil is slightly dilated and always larger than its fellow; reliable information as to the shape and relative size of the the unilateral Argyll Robertson pupil is always smaller. A few of the common conditions Although in the tonic pupil the reaction to light seems ab are considered here. The reaction of the pupil on convergence is sluggish with a long latent period and is Abnormal Reactions of the Pupil unduly sustained. As mentioned pine; the Argyll Robertson pupil does not; fnally, the tonic earlier, loss of light refexes results from a lesion in the retina pupil constricts with 0. A lesion in the third due to the pupil size, which do not last longer than a few nerve abolishes both light and convergence refexes. The affected More complex lesions may result from damage to the eye usually has a slight accommodative paresis and astheno relay paths in the tectum between the afferent and efferent pia is often induced by near effort. The most important of these is the Argyll Robertson get the two eyes to work together when reading and are best pupil, usually caused by a lesion, almost invariably syphilitic, advised to use dilute pilocarpine and fx with the other eye. Any opaci Diffuse illumination allows an observer to obtain a direct ties in the pupillary area can be seen by inspection, aided by and tangential view of the anterior segment of the eye. The Diffuse illumination allows determination of general fea haze is much more pronounced in an old person and the tures, such as colour, size and relative position of structures. This is followed by tangential illumination with a large It is probable that the patient has a cataract, but examina angle of illumination, which helps to increase contrast and tion by distant direct ophthalmoscopy shows a clear red highlight the texture of ocular tissues. The explanation is that the refractive index of the lens substance increases with age, and scattering of light from its surface is greater. The milkiness is due to rays Focal Illumination of light which are refected from the lens and enter the Focal illumination is used for direct observation of the observer’s eye. Various forms of cataract are view of the eye illuminated by a slit-lamp beam of light of diagnosed according to their distribution and nature but moderate width, entering the eye from the left side. Opti observation must always be confrmed by ophthalmoscopic cally the homogeneous media appear quite black; struc examination, and the opacities localized with the help of the tures such as the cornea, lens and suspended particles in slit-lamp (see Figs 11. On the left the pupil, looking as if it were on the surface of the lens, of both Fig. The black space on the right is the anterior appearance over the whole pupillary area suggests a total or chamber. A mature cataract; if it is yellowish-white, with white spots of dim central interval can be distinguished, formed by the calcifcation and the iris is tremulous, a shrunken calcare embryonic nucleus with its Y-sutures. Finally, the pupil may the successive ‘zones of discontinuity’— the fetal nucleus, be blocked with uveal exudates forming an infammatory the infantile nucleus, the adult nucleus and the cortex. Ocular problems can be identifed by different meth ods of examination, which differ in the positioning of the illuminating light and the angle between the illumination and observation arms. Various permutations and combina tions of these techniques are used, some simultaneously and others sequentially. Specular Refection Specular refection allows the observer to visualize the cor neal endothelium by viewing light refected back from this interface. The illuminating and viewing arms are adjusted so that each forms an angle of about 30° to the central per pendicular, the slit-lamp beam is narrowed to a height of 2 mm and focused onto the central corneal endothelium. This is placed immediately adjacent to the refection of the slit-lamp bulb on the cornea. A golden sheen with darker lines outlining the hexagonal endothelial cells is seen (Fig. This light is totally internally refected through the thickness of the cornea, like a fbre-optic light pipe, and emerges at the opposite limbus. The fundal glow highlights the pre Tonometry is the assessment of the intraocular pressure of the sence of opacities in the media, such as cataracts (Fig. It also highlights the presence of Subjective method: It may be done digitally in the defects in the integrity of the normally opaque iris. The light refected off the iris allows Instruments known as tonometers have been devised for visualization of subtle, transparent corneal irregularities, such measuring the intraocular pressure of the intact eye and are as ghost vessels or keratic precipitates. An assistant the nearest mm Hg for the different weight of the Schiøtz may separate the lids while you concentrate on proper placement tonometer. If the scale reading is less than 5, your hand against the patient’s facial bones. After anesthetic drops use the nest highest weight that will give a reading of 5 or are instilled, the patient will not experience any pain from this more. It is important to have a relaxed patient because squinting and blepharospasm may interfere with the reading. Note: Use the above chart to determine the converted reading Gloves should be worn. The depth and the volume of the Rod indentation are dependent on the intraocular pressure and the distensibility of the ocular walls. Housing the instrument is calibrated so that the equivalent read ings in millimetres of mercury can be read off a chart. The Schiötz tonometer is often inaccurate, largely because of wide individual variations in the rigidity of the corneo scleral coats. However, the tonometer is useful for obtain Adjustment knob ing approximate readings, particularly for comparative A(i) A(ii) measurements, such as between the two eyes or for succes sive measurements on the same eye.
Pathologi tion allergy symptoms not allergies discount generic entocort uk, but when dead allergy symptoms phlegm in throat proven entocort 200mcg, they produce focal infammation with cally food allergy testing zurich entocort 100mcg without prescription, the characteristic feature is a wide area of necrosis of reactive destruction of the tissues wheat allergy symptoms joint pain generic entocort 100 mcg visa. In the used in conjunction with sulphatriad (sulphadiazine allergy medicine safe pregnancy order entocort 200mcg fast delivery, sul choroid the vessels become attenuated and there is perivas phathiazole and sulphamerazine) in a dosage of three cular sheathing allergy testing kits for physicians purchase entocort online now. Citrovorum factor (3 mg) or carbamazine which is effective against microflariae, and folinic acid is necessary weekly. Clindamycin is given for 4 weeks in oral doses tinuous non-pulsed delivery of diethylcarbamazine at a of 300 mg 6 hourly along with sulphadiazine prescribed as critical low dosage may succeed in killing the microflariae an initial loading dose of 2 g followed by 1 g 6 hourly. However, due to unacceptable side effects, these two sulphamethoxazole (160 mg/800 mg) twice daily with or drugs have been replaced with ivermectin. Cycloplegics and Onchocerca volvulus may be reduced by effcient larvicidal topical steroids are used to control any anterior segment measures to control the insect vector. It can produce a violent uveitis presenting as ent subsets of disease which differ in presentation and endophthalmitis. The live cysticercus present in the vitre management, but all four are associated with uveitis in ous cavity or located subretinally causes little reaction, some form. There is a strong likelihood of accompa matoid arthritis is in fact the least common. Ocular involvement is common (50% of patients), predominantly manifesting as a bilateral Ankylosing Spondylitis and Uveitis chronic uveitis of insidious onset, often with minimal signs Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic, progressive, pau such as mild pain and redness. The disease is chronic, often ciarticular (involvement of four or less than four joints) missed unless specifcally looked for, and leads to compli disorder involving the sacroiliac and the posterior interver cations such as glaucoma, cataract, posterior synechiae, tebral joints. The onset is insidious with intermittent attacks pars planitis and band keratopathy. This group is affected by Acute, recurrent iridocyclitis is part of the syndrome an acute unilateral iritis of sudden onset, which is generally (25% of patients). The disease lasts 10–20 years and usu self-limited, resolving with treatment in few weeks. Ocular involvement is uncommon this syndrome affects young males and is associated with but iritis has been reported to occur. Rheumatic manifestations (pauciarticular pattern usually affecting Behçet Syndrome large joints) occur in 98% of patients, genitourinary in this is a serious condition with an immunological basis in 74%, ophthalmic in 58% and mucocutaneous in 42%. It which severe iridocyclitis, usually characterized by a hypo tends to affect patients who present with non-specifc ure pyon, is associated with evidence of obliterative retinal thritis, postgonococcal urethritis or dysentery. It is accompanied by ulcerative lesions in the have been isolated from the urethral discharge in about conjunctival, oral and genital mucosae, together with neu 50% of cases. There is an association with dysentery due rological and articular manifestations. This syndrome belongs with Reiter disease requires administration of oral tetracy to the broad category of connective tissue disorders but is cline in a dosage of 500 mg four times a day. It is also probably of two types: the frst associated with herpetiform essential that all sexual partners be examined for genital ulcers in the mouth and the second with aphthous ulcers infection. Alternatively, the Ophthalmic involvement is in the form of a recurrent syndrome may be initiated by a viral infection and perpetu acute iridocyclitis which responds to conventional ated by autoimmune phenomena. No specifc treatment Chapter | 17 Diseases of the Uveal Tract 251 is known and only non-specifc measures are available such Uveitis Associated with Vitiligo, Poliosis and as systemic steroids or immunosuppressives. Deafness (Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada Syndrome) Sarcoidosis this is a rare bilateral condition in Caucasians, but com Boeck sarcoid is a systemic disease manifested by infltra moner in pigmented races—Asians, Hispanics and Africans. Originally separately categorized granulomata, which either resolve or are replaced by hya as Vogt–Koyanagi syndrome (poliosis, vitiligo, alopecia linized scar tissue. It is frequently complicated by a granu and chronic anterior uveitis) and Harada disease (bilateral lomatous iridocyclitis. There is a chronic granulomatous iridocyclitis, with sarcoidosis in association with hilar lymphadenopathy an exudative choroiditis, which often leads to an exudative and erythema nodosum. Chronic iridocyclitis, where multiple discrete granu companied by a patchy depigmentation of the skin and lomata develop in the iris in older individuals; it has a whitening of the hair, eyebrows and eyelashes (poliosis). Infammation is controlled with high ally associated with granulomata in the retina. Uveoparotid fever or Heerfordt’s disease, which is bilat gradually tapered over months to years. In case steroids fail eral and characterized by a simultaneous involvement to produce an adequate clinical response, or if the patient of the entire uveal tract, parotid gland and frequently cannot tolerate their side effects, cytotoxic and immunosup the cranial nerves. Approximately half the cases com Sympathetic Ophthalmitis mence with a granulomatous iridocyclitis and half with See Chapter 24, Injuries of the Eye. The Heterochromic Iridocyclitis of Fuchs disease is self-limiting although the iridocyclitis may this is a low-grade chronic cyclitis, the only apparent fea cause permanent visual damage. The parotid swellings tures of which are a lightening of the colour of the affected last for 6 weeks to 2 years but ultimately subside. The latter distinguish the condition from congenital conjunctival nodules in the lower fornix, calcifcation of heterochromia. The iris becomes atrophic, loses its mark the cornea associated with hypercalcaemia and keratocon ings and readily transilluminates in circumscribed areas, junctivitis sicca. The condition is usually the diagnosis is made by the presence of other systemic said to be associated with some disturbance of the sympa manifestations such as pulmonary changes and areas thetic nerve supply which controls the chromatophores, of rarefaction in the bones. Investigations include a chest accounting for the depigmentation and the tone of the X-ray, gallium scan of the head, neck and mediastinum blood vessels. When the blood vessels are dilated, white for increased uptake, detection of raised levels of serum cells escape and get deposited on the cornea as precipitates. During cataract surgery, fne fli linaemia and biopsy of the skin or conjunctival nodules, form haemorrhage from the opposite angle has been noticed palpebral lobe of the lacrimal gland if enlarged, lymph node to occur as soon as the anterior chamber is opened—this is or lung. Patients with sarcoidosis often fail to react to an intradermal injection of tuberculin indicating a disturbance this is a distinct clinical entity of unknown aetiology in of immune function. In the Kveim test, the skin of patients which there are acute, recurring, well-defned lesions af with sarcoidosis responds to an injection of a suspension of fecting the pigment epithelium. The usual corresponding to the initial halo-like zone can eventually symptom is blurring of vision. During the sev Epitheliopathy eral months of evolution of the lesion, there is no change in its shape or size. Acute lesions last weeks to months but this disease affects both the eyes in healthy subjects of the disease has a chronic, recurring course. Spontane over several years and is characterized by the occurrence of ous resolution with good visual recovery is usual, although further acute lesions. Over the next the primary lesion appears to be an obstructive vasculi 3 months, pigment epithelial and retinal swellings subside this at the level of the choriocapillaris resulting in ischaemic and the centre of the lesion takes on a grey appearance with injury and focal swelling of the retinal pigment epithelial a lighter coloured margin. This gives rise to the characteristic ophthalmoscopic stage shows a relative hyperfuorescence at the margin appearance of cream-coloured placoid lesions over the of the lesion, while the centre of the lesion remains hypo posterior pole within the equatorial region. After 3 months, fuorescein studies show uni angiography shows patchy, irregular choroidal flling, form hyperfuorescence of the lesion lasting throughout gradually outlining these lesions which mask the back the angiogram. Each area is stained with fuorescein epithelium and choriocapillaris but the larger choroidal ves during the later stages without signifcant leakage of dye. The margin of the lesion is clearly Upper respiratory symptoms, altered sensitivity to drugs defned, with regular hyperpigmentation. The differential and increased levels of gamma globulin favour a viral or an diagnosis is choroidal sclerosis, placoid pigment epitheli immune complex mechanism. The differential diagnosis opathy, pigment epithelitis and serpiginous choroidopathy. The clinical picture resembles lium is permanent but changes in the choriocapillaris are an insidiously disseminated choroiditis characterized by minimal. The Masquerade Syndromes macula is frequently involved with peripapillary and macu lar geographic lesions. Fluorescein angiography and histo these include a group of diseases which mimic anterior or logical studies reveal disappearance of the choriocapillaris posterior uveitis in their clinical features but the aetiopatho and the pigment epithelium. Ophthalmoscopy shows small, genesis is entirely different, being usually neoplastic or greyish, disc-like or circular confuent lesions and choroi occasionally ischaemic. Acute leukaemia, iris melanoma, dal scars with slight pigment dispersion, leading to depig juvenile xanthogranuloma, small round cell malignancies, mentation in a serpiginous confguration. Immunosuppressives may be indicated in cases in general uveitis, cytological and immunohistological where the macula is threatened. The lesions form in two or four clusters in the blood supply of the uveal tract is derived almost the macular area and may be unilateral or bilateral. Fluorescein angiographic fnd peculiar distribution resulting in the formation of the major ings are minimal in the acute stage but hyperfuorescence arterial circle of the iris causes involvement of both the iris Chapter | 17 Diseases of the Uveal Tract 253 and the ciliary body in pathological vascular conditions. Central Serous Choroidopathy l the aim of treatment is to produce a burn just sufficient Central serous choroidopathy (Fig. Clinical features: Serous detachment of the macula in young patients with l Preferentially in young males a demonstrable leak fattens more rapidly after argon laser l Sudden onset treatment but the prognosis for ultimate visual acuity is not l Blurring of vision accompanied by a positive scotoma improved. Complications that can occur following central Examination and management: serous retinopathy are geographic atrophy of the pigment epithelium and choriocapillaris, invasion of the subpigment l There is a circular swelling seen in the macular area epithelial space by new vessels with progression to a fbro usually about the size of the optic disc. It is characterized by the development of new, common and may occur in the form of small triangular branching and enlarged vessels in the iris (Fig. Irregular lacunae in the pigmen the neovascularization being frequently accentuated towards tary epithelium may often be seen with retroillumination its root and in the angle of the anterior chamber. A rise in intraocular Essential (Progressive) Atrophy of the Iris pressure occurs, initially with an open anterior chamber this disease of unknown aetiology is characterized by a angle showing neovascularization, but later as fbrosis takes slowly progressive atrophic change in the tissues of the iris, place the angle zips up, leading to an intractable neovascu which leads to the complete disappearance of large portions lar glaucoma. It forms part of the iridocorneal endothelial retina prevents the development of neovascular glaucoma. Contraction of the membrane with adjuvant administration of mitomycin C or a drainage produces synechiae, corectopia, iris atrophy from ischaemia, implant is used to control the raised intraocular pressure. Uveal Effusion Syndrome A diagnosis of idiopathic uveal effusion syndrome is made Iridoschisis after excluding all other infammatory and hydrostatic this rare condition occurs most commonly as a degenera causes of uveal effusion. The basic pathogenesis is a tran tive ageing senile phenomenon, though it may follow as a sudation of fuid from the vascular uvea with extravasation late result of severe trauma. Large dehiscences appear on from the choriocapillaris into the suprachoroidal space and the anterior mesodermal layer of the iris and strands of this within the uveal tissues. The result is bilateral choroidal tissue may foat into the anterior chamber as if teased out and ciliochoroidal effusion and subsequent detachment; in by a needle; occasionally extensive areas of this layer may severe cases, a secondary serous retinal detachment occurs. A high incidence of glaucoma (almost Cells may be present in the vitreous and dilated episcleral 50%) is reported and is usually of the angle-closure type. The latter include conditions such as arteriovenous fstula, nanophthalmos with a thickened sclera, and diseases with combined in fammatory and hydrostatic mechanisms such as tears of the retinal pigment epithelium, following cataract, glau coma or retinal detachment surgery with infammation and hypotony, excessive laser treatment or cryotherapy and supra-choroidal haemorrhage. The condition is known to resolve spontaneously fol lowing which the retinal pigment epithelium shows patchy ‘leopard spot’ changes. Chapter | 17 Diseases of the Uveal Tract 255 rubbing of the posterior surface of the iris against the zonules of the lens. The mid-peripheral iris is concave anteriorly, with radial transillumination defects in the iris. Melanin from the iris neuroepithelium is phagocytosed by the corneal endothelial cells, seen on slit-lamp examina tion as a vertical spindle (Krukenberg spindle). There is deposition of melanin pigment in the trabecular meshwork (Sampaolesi line) and glaucoma. Degenerative Changes in the Choroid Degenerative conditions are more frequent and important in the posterior than the anterior part of the uveal tract. Secondary Degenerations Those following infammatory lesions culminating in localized spots of complete atrophy have already been considered. The loss of nourishment to the retina causes atrophy of the outer layers and migration of pigment from the pigment epithelium into the more superfcial parts of the retina. The pigment tends to get deposited in the peri vascular spaces of the veins, so that the retinal veins may be mapped out here and there by pigment. More noticeable ophthalmoscopically are jet-black branched spots of pig ment resembling bone corpuscles and standing out in sharp relief—an appearance seen in its most typical form in pig mentary retinal dystrophy. On the temporal side the choroidal and scleral crescents are Primary Choroidal Degenerations delineated. Note the oblique temporal direction of the optic nerve fibres and the overlapping on the nasal side resulting in supertraction. The localized forms are usually central, although circumpapillary changes around the disc are not infrequent in myopia or the late stages of glaucoma. In the majority of cases of moderate myopia, there is a Central choroidal atrophy is most commonly the result myopic crescent (Fig. This is a white crescent at of myopia or obliterative vasosclerosis, essentially a change the temporal border of the disc; very rarely it may be nasal. In high degrees of myopia it may extend to the upper and Myopic choroidoretinal degeneration. Anatomically there is consider stretching but are primary in nature and genetic factors play able distortion of the disc. They have been errone epithelium stops short at a variable distance from the disc ously described as ‘myopic choroiditis’ but the condition and here the choroid is atrophic (Fig. They do not run parallel to the degree the retina, including the pigment epithelium, encroaches of myopia and tend to occur after mid-adult life, whereas over the nasal edge of the disc (supertraction crescent). There is a gradual disap ably involve both the ectodermal (retinal) and mesodermal pearance of the small vessels of the choroid with the devel (choroidal and scleral) tissues. The condition is a hereditary degeneration and the most prominent symptoms are night-blindness and extreme con centric contraction of the visual felds. In certain patients these may not be two separate disease entities but may represent a continuum of a spectrum of which may extend to the region of the disc, where they clinical manifestations. The exudative or wet type of macu may eventually fuse with each other and with the myopic lar degeneration is due to leakage of fuid from a neovascu crescent so as to form an irregular circumpapillary ring.
The port is usually buried on the upper lateral chest allergy shots reddit entocort 100 mcg free shipping, away from the shoulder joint and breast tissue allergy treatment home remedies india generic entocort 200mcg free shipping. If the thrombophilia screen is abnormal allergy shots yearly purchase entocort 100 mcg otc, discuss with Paediatric Consultant and Haematologist allergy medicine ok for high blood pressure discount entocort 100mcg without a prescription. Consider also whether a blind lavage or bronchoscopy should be performed at the time of anaesthesia to obtain material for culture; also discuss with the paediatric consultant (Jane Davies) as bronchoscopy allergy medicine dosage for babies discount entocort 200 mcg with visa, lavage and endobronchial biopsy may be performed for research purposes once consent obtained allergy symptoms 4 year old buy entocort cheap online. Post insertion Chest x-ray done and looked at for line position and pneumothorax. There is some evidence that using the port to take blood samples increases the risk of line infection. Consider the use of fingerpricks where possible, and discuss with an experienced nurse specialist or Consultant. Complications – Failure to access port – difficulty may be due to lack of experience. After cultures have been taken, systemic antibiotics via another route and possibly injecting vancomycin or teicoplanin into the system may work. Blood cultures and an echocardiogram may help the diagnosis and sometimes radio-opaque contrast can collect in a thrombus if injected down the line. Beware of injecting into a line that may have thrombus around it you may cause pulmonary embolism, so think first and be careful. Remember that one of the commonest causes of pulmonary emboli in children is an endovascular foreign body. Catheter fracture has been reported after a road traffic accident in a child wearing a seat belt. For severe bronchospasm, dose is 2 mg/kg prednisolone administered in the morning after food, which will be reduced as soon as possible, depending on the response. We sometimes use intravenous methylprednisolone 10-15 mg/kg/day (max dose 1gm) for 3 days, repeated monthly – for severe cases and when compliance with oral prednisolone is an issue. Exposure to chicken-pox in a child who has not yet had it, may require varicella-zoster immunoglobulin (see section 10. If a child is on long term oral steroids itraconazole will usually be given in case there is exposure to aspergillus. Although in theory it would seem useful due to the nature of the persistent lung inflammation, benefit has not been proven. We use budesonide or fluticasone, and occasionally ciclesonide (with its small particle size), but not usually beclometasone. Devices used depend on the age of the child, but nebulised steroids are rarely used. High doses of inhaled steroids are preferably given via a spacer device to reduce mouth deposition and potential systemic side effects. Always consider whether the dose can be reduced whenever the child is seen in clinic, or indeed stopped. Our intention is that it would be for unusual for a child aged 6 and above not be commenced on it. There is some evidence for prophylactic benefit as a trial of use in 6-10 year olds with near normal lung function showing a reduction in exacerbation rate and a halt in deterioration of lung function. There seems to be no clinical difference between daily and alternate days treatment but we mostly use daily dosing. A new prescription will be given by our pharmacy, with future prescriptions via the home delivery service (and we are still reimbursed). There is a good correlation between response at 3 months and that seen after 12 months treatment. We almost always use 7% (but not higher concentration) as it is superior to 3% if tolerated. Its mode of action is to osmotically draw water into the airways to hydrate the mucous and aid clearance. Always give salbutamol 2-4 puffs of 200 mcg before every dose and spirometry must be performed before and after the first dose in hospital prior to home therapy. The new AeroEclipse breath actuated nebuliser nebulises to dry but there is no comparative efficacy data currently. May have to titrate up from 3% in younger children and those who don’t initially tolerate 7%. To date, two published trials and two phase 3 studies suggest that it may 83 Clinical guidelines for the care of children with cystic fibrosis 2017 Comes in 40 mg gelatine capsules so 10 capsules via specific inhaler device quite an onerous therapy. Up to 25% have significant bronchoconstriction despite salbutamol precluding its routine use. Response: Highly individual, some really respond well, others effectively zero so a therapeutic trial and outcome monitoring is important. Inhaled Dry Powder Mannitol is only licensed in adult 18 years and above and not currently included in the clinical commissioning policy for children. It is believed to be effective in those with and without chronic Pseudomonas infection. Dosage: 250 mg once daily (<40kg) or 500 mg once daily (≥40kg) three times a week (Mon Wed Fri). Judgement of response: Onset of action is slow (at least 2 months) and a minimum 4, preferably 6 month trial is required. Liver function tests should be performed at any time blood is being taken for other reasons and at annual assessment. Use of azithromycin and erythromycin (prokinetic) long term should be avoided due to potential additive side effects. All eligible patients in our clinic were commenced on this oral preparation, which is planned for long-term, uninterrupted use. The drug has since been approved for the other known gating mutations (G178R, S549N, S549R, G551S, G1244E, S1251N, S1255P, G1349D). Funding for the granule formulation has now been agreed (Dec 2016) for children aged 2-5 years with the same group of mutations. We should be aware of everyone’s genotype at diagnosis and nd prepare for starting treatment on or shortly after their 2 birthday. Class 3, the ‘gating’ mutations lead to channels which are not open often enough, and when open are open for shorter time periods; the commonest of these is G551D. Trials have confirmed more modest efficacy in adults with the class 4 (conductance) mutation R117H, but efficacy was not evident in children for whom the drug is not licensed in Europe. Ivacaftor is administered twice daily and it is crucial that it is taken with or very shortly after a high-fat meal or snack (with the usual pancreatic enzymes if used), as otherwise absorption is poor. Dose reduction recommendations are available for patients with significant hepatic or renal impairment. However cases of non-congenital lens opacities without impact on vision have been reported in paediatric patients treated with ivacaftor. Although other risk factors were present in some cases (such as corticosteroid use and exposure to radiation), a possible risk attributable to ivacaftor cannot be excluded. Baseline and follow-up ophthalmological examinations (annually in those under 12 years) are recommended in paediatric patients initiating ivacaftor treatment. Drug interactions: There are some significant interactions, most importantly: Azole antibiotics: (itraconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole) lead to inhibition of the breakdown pathways of ivacaftor and accumulation of the drug. Due to the very high cost of the drug, the Commissioners in England have mandated monitoring and have imposed stopping criteria. If no explanation is found, the sweat test should be repeated the following week and ivacaftor stopped if there is still an inadequate change. Experience has now shown though that clinical response does not correlate with sweat chloride changes. Please ensure that Prof Jane Davies is informed before a new patient is commenced on treatment. Small numbers of patients may be receiving Orkambi through a named patient programme. In general, we advise avoidance of situations where there can be high levels of this fungus: mucking out stables (it is commonly found in damp hay), building sites (common when knocking down old buildings), and exposure to compost (heaps and bags). In general, if children insist on horse riding this must be done out in the open, and they should avoid being inside the actual stable. Atypical cases may lack some or all of these criteria – maintain a high index of suspicion, and discuss with the Consultant if in doubt. Note though that in some cases who do well, the IgE does not fall, so treat the patient not just the IgE level. Inhaled and nebulised corticosteroids are used by some, but not by us – there is no evidence for their use. This is attractive for the non-adherent patient, and may have fewer side-effects, at the cost of more inconvenience. The 3-day pulses are 88 Clinical guidelines for the care of children with cystic fibrosis 2017 Decision to use should be discussed with the consultant, but this is increasingly our preferred option. For patients <12 years give 5mg/kg bd (max 200mg bd), or >12 years 200 mg bd orally (monitor liver function) and continue whilst they remain on steroids. The capsules are poorly absorbed and are a last resort (as the liquid has a poor taste so may be refused), they must be taken with acidic drinks. It should also be given to anyone taking oral steroids (for whatever reason) if there is any suggestion of concomitant aspergillus infection while they are taking the steroids. However levels may still be indicated if there are concerns that a patient is not responding adequately to treatment; about toxicity; they are taking capsule form; or if interacting drugs are introduced. If not, consider increasing dose nd before changing to our 2 line agent posaconazole (see below) taking note of any sensitivities available. It is an alternative when itraconazole is not tolerated or effective and it is critical to treat the patient with a second line agent. It would be prudent, before changing to posaconazole, to check to see if the serum level of itraconazole 89 Clinical guidelines for the care of children with cystic fibrosis 2017 Blood levels must be obtained when initiating therapy as there is still little published dosing information in children. It is not licensed for children under 18 years so it is a consultant decision to use in older children. Posaconazole levels Pre-dose sample may be taken after patient has been taking for at least 1 week. Relapses st Relapse is common, be alert to this possibility even up to 2-3 years after 1 episode. High doses of steroids may be needed for a long time, but the aim is always to try to use as short a course as possible so close follow up is needed. A repeat course of antifungals will also be required as per guidance above, in some cases posaconazole may be considered first in preference to itraconazole for relapses, but this will be dependent on time from last episode and is a consultant decision. If it essential to use it, and the child does not tolerate the normal amphotericin, consider using nebulised liposomal amphotericin; note the high cost. Post script we have now stopped using voriconazole Whilst it has better absorption than itraconazole and is not affected by gastric pH, its use is limited by side effects, particularly severe photosensitivity (in some cases despite use of high factor sun screen). Liver function tests are mandatory (weekly for the first month and then monthly thereafter), and must not be forgotten. Similarly to itraconazole, adrenal suppression has been reported in patients on voriconazole also taking inhaled corticosteroids. Voriconazole levels Pre-dose sample may be taken after patient has been taking for at least 3 days Range: 1. We would treat this with a three-month course of itraconazole in the first instance. If symptoms return on stopping the itraconazole a course of posaconazole nd would be 2 line. It is heralded by worsening of symptoms and progression of x-ray shadows, sometimes with cavitation, haemoptysis and pleuritic pains. Indications for intravenous antifungal therapy this is a consultant decision only and is made after consultation with microbiology. Similarly to Aspergillus it can cause fungal balls in cavities and can be found in paranasal sinuses. Clinical implications are poorly understood; it is often not associated with symptoms. We are now much more likely to consider early attempts at eradication especially if symptomatic but only after treatment for other causes of cough or exacerbation have been treated and excluded. The microbiology lab will supply azole sensitivities and treatment may be guided by these when available, although we would still try to avoid voriconazole because of the side effect profile. Do not forget to ask about perineal Candida, it is common in infants with nappy rash and can be present in older children. The source is usually from hypertrophied tortuous bronchial arteries supplying areas of chronic airway inflammation. S aureus is the one bacterium that has been identified to be associated with an increased likelihood of massive haemoptysis. Massive, profuse haemoptysis due to vessel rupture can be life threatening (>250 mls/24 hours is the conventional level, but anything more than half a cupful over 24 hours merits referral). Bad haemoptysis is usually seen in patients with bad lung function, but has been reported in patients with normal spirometry. The patient may experience a gurgling sensation which is a 92 Clinical guidelines for the care of children with cystic fibrosis 2017 Primary management is resuscitation if needed (incredibly rare) lay patient on side (gurgling side down), give oxygen. Initial management – Mild haemoptysis with an infective exacerbation will normally settle without specific intervention.
Discount 200mcg entocort amex. Treatment Of Allergy Allergy Ka Ilaj علاج الحساسية.