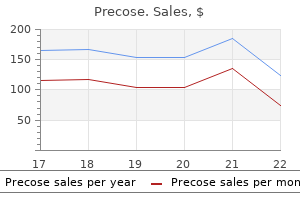
Eloise J. Prijoles, M.D.
- Greenwood Genetic Center
- Columbia, South Carolina
Metastasis Key: A References: the Requisites xylitol blood glucose buy 25 mg precose overnight delivery, Neuroradiology; Third Edition diabetes symptoms pdf best 50mg precose, Mosby Elsevier 2010 560-561 diabetes mellitus jokes buy precose 50mg without prescription. The most common intrdural extramedullary lesion of the spine is a meningioma or schwannoma diabetic ketoacidosis in cats discount precose generic. Though leptomeningeal metastasis are seem in the intradural extramedullary space diabetes type 1 kidney disease generic precose 25 mg with amex, meningiomas are more common report diabetes medications ‘worse than disease’ purchase cheap precose. Meningioma Key: A References: the Requisites, Neuroradiology; Third Edition, Mosby Elsevier 2010 384, 399-401. Astrocytomas are parenchymal lesions found in the intraxial compartment of the brain. Oligodendroglioma Key: A References: the Requisites, Neuroradiology; Third Edition, Mosby Elsevier 2010: p. Oligodendrigliomas are glial neoplasms that are not cystic and do not occur in the suprasellar region. Machiafava Bignami Disease is in the differential of collosal lesions but patients with this disease have a history of alcoholism. The disease affects the body of the corpus callosum first followed by the genu and then the splenium of the corpus callosum. It typically involves the subcortical U fibers of the anteroinferior temporal lobes, subinsular region, external capsule zones and inferior frontal lobes. The location of the lesions and the presentation are consistent with white matter shear injury as seen in Diffuse axonal Injury in the setting of trauma. Lupus Cerbritis should be considered in a female of reproductive age with a complicated neurologic presentation. Multifocal Cerebral Infarction would not be expected to resolve two weeks post therapy as stated in this case. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy is a disease of older patients that presents with foci of hypointensity on susceptibility weighted imaging and hemorrhage. Meningiomas are the most common extra axial neoplasms of the brain that arises from the dura and are associated with an enhancing dural tail which is seen in 72 percent of patients with meningiomas. Oligodendrigliomas are intraxial lesions that occur in the frontal lobes most commonly that are associated with calcification but do not involve the dura. Metastatic disease can involve the dura either via direct extension from the bone or via hematogenous spread. A dural tail in association with a dural metastasis can be seen though not considered characteristic of this entity. Key: A References: the Requisites, Neuroradiology; Third Edition, Mosby Elsevier 2010: p. Focal motor seizures are followed by progressive loss of ipsilateral motor function associated with cognitive decline. Glomus jugulare Key: A References: the Requisites, Neuroradiology; Third Edition, Mosby Elsevier 2010: p. The most common location of paragangliomas in the head and neck is at the level of the carotid body. Though a location of paragangliomas, the carotid body paraganglioma is the most common. Glomus Jugulare is a location/type of paraganglioma occurring at the level of the jugular foramen but the carotid body is the more common location. This is secondary to adjacent inflammation at the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons (De Quervains tenosynovitis). The periosteal reaction of osteomyelitis is usually associated with abnormal underlying bone. The periosteal reaction of hypertrophic osteoarthropathy is more diffuse involving both the radius and ulna. Anterior cruciate ligament Key: D Rationale: There is a Segond fracture, an avulsion fracture at the lateral aspect of the proximal tibia at the site of capsular attachment with contributing oblique fibers from the lateral collateral ligament and iliotibial band, related to varus stress with an accompanying twisting injury. If the force generated is great enough, injury may result in dorsal dislocation of the capitate, with scapholunate dissociation or scaphoid fracture, a perilunate dislocation. You are shown an axial fat-suppressed fast spin echo T2-weighted image of a 16-year-old boy following knee trauma. Rationale: There is impaction at the medial patella and contusion at the lateral aspect of the lateral femoral condyle with thickening and abnormal signal of the medial patellar retinaculum/medial patellofemoral ligament. This is secondary to impaction following spontaneous reduction of a lateral patellofemoral dislocation. Posterior talofibular Key: B Rationale: Inversion injuries of the ankle tend to affect the anterior talofibular ligament first, followed by the calcaneofibular ligament. This is why we so commonly see isolated chronic sprain of the anterior talofibular ligament or chronic sprain of both the anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments. Parosteal Key: A Rationale: Osteosarcoma secondary to underlying pathology or radiation has the worst prognosis. The prognosis of telangiectatic osteosarcoma is similar to that of the more common subtype. Periosteal osteosarcoma and paraosteal osteosarcoma have a much better prognosis, both being lower grade tumors. Transient osteoporosis of the hip (a focal phenomenon secondary to underlying stress fracture) involves the head and neck only, with no clearly defined advancing edge. Key: B Rationale: the humeral head is dislocated inferiorly with the arm held in an abducted position. Luxatio erecta or inferior shoulder dislocation is the least common type of glenohumeral dislocation. What is one of the characteristic radiographic findings of erosive osteoarthritis Central erosion Key: D Rationale: the characteristic radiographic appearance of erosive osteoarthritis reflects osteoarthritis (joint space narrowing, osteophyte formation, subchondral sclerosis) and central erosion, all of which contributes to the "gull-wing" configuration. Scattered mitosis and hypercellularity D Diffuse high-signal intensity on T2W images Key: A Rationale: There is a soft tissue mass at the plantar aspect of the metatarsal heads at the third webspace. This is not a true peripheral nerve sheath tumor but rather a mass of inflammation, fibrosis and torn peripheral nerve, a sequela of a compression neuropathy. There is scintigraphic evidence of diffuse peritonitis Key: A References: nd Bennet P, Oza, U. Images of the abdomen and pelvis show free spillage of the tracer into the peritoneal catheter. These findings confirm a patent shunt from the reservoir to the peritoneal cavity. The activity courses normally through the efferent limb as shown on the anterior chest and abdomen images. The final image of the abdomen and pelvis shows dissipation of the tracer throughout the peritoneal cavity. This study is not used to diagnose peritonitis or other inflammatory/infectious process. Insensitivity of forearm bone density measurement secondary to preponderance of cortical bone C. Underestimation of the bone density in the spine and hip secondary to arthritic changes D. The forearm has more cortical bone than the spine and hip, which have more cancellous bone. Forearm evaluation is indicated in patients with hyperparathyroidism, which primarily affects cortical bone as well as patients who are obese or have spinal/hip hardware. Arthritic changes are associated with falsely increased bone mineral density in the setting of osteophyte formation and sclerotic changes. The distal forearm is the correct area to scan so that would not explain the differences in density. If a prior radioisotope study was performed, excreted tracer from that study could falsely elevate the urinary activity creating a false negative exam. There is not enough information to know if this would cause a normal or abnormal result. Vitamin B-12 is administered for the exam, so concurrent use would not affect the test. The typical pattern of Alzheimer disease hypometabolism is temporal and parietal lobe involvement. As the name implies, the hypometabolism is present in the frontal and temporal lobes. Many readers prefer intrinsic comparison to blood pool and hepatic activity as cut-offs. Concerning the use of extremity radiation badges in Nuclear Medicine procedures, which one of the following describes the correct placement of a ring badge What is the maximum allowable total effective dose equivalent annual occupational radiation exposure for an adult Dipyridamole should be administered with caution in patients with a history of reactive airway disease or severe obstructive pulmonary disease. Adenosine should be administered with caution in patients with a history of reactive airway disease or severe obstructive pulmonary disease. Dobutamine is the preferred agent for pharmacologic stress in patients with a history of significant reactive airway disease or severe obstructive pulmonary disease. Aminophylline should be available for the treatment of vasodilator-induced bronchospasm. Imaging of neonatal gastrointestinal obstruction, Radiol Clin North Amer, 1999; 37(6):1163-1186. Rationale: Findings: the contrast enema demonstrates a zone of transition, with a normal caliber rectum, and a dilated proximal sigmoid and descending colon. A large meconium plug is also present, but the presence of the zone of transition is consistent with the diagnosis of Hirschsprung disease. The enema is typical of Hirschsprung disease, and the most appropriate next step is confirmation with rectal biopsy. A colostomy may be necessary before definitive management with pull-through procedure, but would only be done after confirmation of the findings with biopsy. The most appropriate subsequent step is confirmation with rectal biopsy; a pull-through procedure would be the eventual surgical repair, after diagnosis is established. The enema findings are consistent with Hirschsprung disease, and the most appropriate next step is confirmation with rectal biopsy. The Dandy Walker malformation is characterized by torcula-lambdoid inversion, reflecting the elevation of the tentorium cerebelli. Microcolon is a term used to describe an unused colon, and therefore it is seen in cases of distal atresia. In patients with duodenal atresia, sufficient succus entericus is generated by the bowel distal to the duodenal atresia to allow development of a normal caliber colon. This syndrome causes obstruction at the level of the colon, and therefore it is not associated with a microcolon. Meconium ileus is an obstruction of the distal small bowel, caused by abnormal, inspissated meconium, typically in patients with cystic fibrosis. Because the obstruction is in the distal small bowel, the colon will be unused, will be small, and termed microcolon. Short-segment Hirschsprung disease, like meconium plug syndrome, is an obstruction at the level of the colon, and therefore it is not associated with a microcolon. A right aortic arch may be seen in a minority of patients with D-transposition, typically less than 10%. Which of the following ovarian masses in children is associated with abnormal sexual development Cystic teratoma is the most common, benign tumor of the ovary, and is not associated with abnormal sexual development. Dysgerminoma is a malignant germ cell tumor, which are not associated with abnormal sexual development. Granulosa cell tumors are the most common malignant neoplasm of sex cord origin and are often hormonally active, presenting with precocious puberty or with menstrual irregularities after puberty. Endodermal sinus tumors, or yolk sac tumors, are germ cell neoplasms which are not associated with abnormal sexual development. A contrast enema is performed on a one-day-old infant presenting with bilious emesis and abdominal distension. Rationale: Findings: the examination shows a microcolon, which is a term applied to an unused colon; this happens in infants with congenital distal bowel obstruction. Patients with Hirschsprung disease should demonstrate a zone of transition between normal caliber colon distally, and dilated colon proximally. The colon is normal in caliber, and demonstrates a large filling defect representing the meconium plug. In patients with small left colon syndrome, the left colon and often portions of the sigmoid are small, similar to a microcolon; however, unlike the findings in the test case, the remainder of the colon, including the rectum, is normal in caliber.
Insert shows external (complete) rectal prolapse (procidentia) with herniation of all layers of the rectal wall diabetes numbers chart purchase precose 50mg on line. Note the low position of the rectum and anus relative to the ischial tuberosities diabetes type 1 beta cells purchase precose 50 mg online. Higher than water density fluid is present within the mesentery and peritoneal recesses diabetes diet us best 25mg precose. At surgery there were several lacerations of small bowel diabetes medications in canada precose 50mg lowest price, and the descending colon had a "degloving" injury with active bleeding diabetic diet kraft 25mg precose. Bortolin M et al: Primary repair or fecal diversion for colorectal injuries after thickness laceration blast: a medical review diabetes definition mayo clinic cheap precose on line. Epub ahead of print, 2009 0 Insertion of foreign objects into rectum may result in 5. The outer rim of the "Mexican hat" is the head of the polyp, while the inner ring is the stalk. In a patient with known diverticulosis, it is often much easier to perform and interpret a single-contrast rather than an air (double) contrast barium enema. When measuring such a lesion, the reported size should optimally be based on the diameter of the "head" rather than the length of the stalk. Note the absence of a colonic obstruction, a typical feature of this soft and compressible tumor. Bozkurt N et al: Adenoma with rectal villous diarrhoea and severe (10%), > 2 cm (53%) hypokalaemia (McKittrick-Wheelock syndrome). Note the short segment, irregular, circumferential narrowing of the lumen with destroyed mucosa and nodular "shoulders. The presence of mesenteric adenopathy adjacent to a colonic mass is strong evidence for lymphatic spread of a primary colon cancer. Cecal carcinoma may mimic appendicitis with cecal wall thickening, infiltrated fat, and distended appendiceal lumen. The presence of a circumferential cecal mass and omental (or liver) metastases indicates a malignant process. Surgery confirmed carcinoma of the sigmoid colon with ischemic colitis of the descending colon. A distal colon cancer is one of the most common causes for colonic obstruction in older adults. Note the short segment, soft tissue density of the wall thickening and luminal narrowing. Note the abrupt and short thickening of the colonic wall and narrowing of the lumen. The clinical and imaging features are typical of a distal colon cancer, though the patient is younger than most affected patients. There was no colonic obstruction, suggesting the soft nature of this villous carcinoma. The dual venous drainage of the rectum (systemic and portal) explains this pattern and results in very different clinical behavior of rectal and colon cancers. This patient had no liver metastases, again emphasizing the unique patterns of spread in rectal vs. Note the adenopathy adjacent to the rectum and the tumor in the sciatic foramen. While these adenomas generally start as sessile lesions, they may be drawn out onto stalks due to the peristaltic force of the bowel. Vitellaro M et al: Risk of desmoid tumours after open and laparoscopic Gross Pathologic & Surgical Features colectomy in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Colonic polyps in familial polyposis can range in number from dozens to thousands, as in this case. While these resemble hyperplastic polyps radiographically, this patient has familial polyposis with adenomatous polyps that have potential for malignant degeneration. There is a large mass in the right rectus muscle that proved to be a desmoid tumor within an incision site. With imaging alone, a benign mucocele may not be distinguished from a mucinous carcinoma. While these findings mimic those of appendicitis, there is much more soft tissue density within the wall than would be expected with simple appendicitis. The patient had a subsequent endoscopic biopsy of the mass, which identified a non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Note the oral contrast filling the lumen of the cecum, indicating the lack of obstruction. It is not possible to distinguish the primary congenital and kidney (splenorenal ligament). It usually develops as 1 (epithelial-lined) cyst from the acquired cyst by imaging, with "fused" mass of tissue, but variations are common. One or more accessory spleens are found in up to 30% of the general population, usually small spherical structures near the Multiple lesions within the spleen are most typically the result splenic hilum. These can enlarge, especially following of a granulomatous process, which may be either infectious splenectomy, and may simulate a neoplastic mass or cause. The spleen may be congenitally absent (asplenia) or have the pancreatic tail usually inserts into the splenic hilum many unfused components (polysplenia). Inflammatory or neoplastic splenic anomalies and are associated with cardiovascular conditions affecting the pancreatic tail can easily invade the anomalies, situs inversus, and other anomalies, often with splenic parenchyma, resulting in intrasplenic pseudocyst, for serious and even life-threatening consequences. Conversely, splenic tumors or an accessory spleen may mimic a pancreatic tail mass. The spleen is rarely on a long mesentery and may be found in any abdominal or pelvic location ("wandering spleen"), placing Splenic infarction is a relatively common cause of acute left it at risk for trauma and torsion with infarction. It appears as a sharply defined, often wedge-shaped zone of minimal enhancement abutting the the spleen is the largest lymphatic organ, the size of which splenic capsule. Patients at risk for infarction include those varies among individuals and even in the same person by with sickle cell disease and those with cardiovascular blood volume, state of nutrition and hydration. A ventricular assist devices are especially prone to embolic calculated splenic index (length x width x breadth) over 480 infarction of the spleen. The average length is up to 12 cm, with a width and breadth of 7 and 4 cm, respectively. The white pulp is the lymphoid tissue and the red is Splenosis is the peritoneal implantation of splenic tissue that composed of the vascular tissue and splenic cords (plates of may follow traumatic rupture of the spleen. Because of its vascularity, the red pulp mistaken for polysplenia or peritoneal implants of tumor enhances rapidly, giving the spleen a very heterogeneous (carcinomatosis). This may be mistaken for splenic pathology but is a usually allow accurate diagnosis. This could be mistaken for a primary pancreatic mass, such as a neuroendocrine tumor. The spleen is of variable shape and size, even within the same individual, varying with states of nutrition and hydration. The medial surface is often quite lobulated as it is interposed between the stomach and the kidney. The tail of the pancreas also inserts into the splenic hilum through the splenorenal ligament. The gastrosplenic ligament carries the short gastric and left gastroepiploic vessels to the stomach and upper portion of the spleen. Splenomegaly is a common abnormality and can be caused by congestion, hematologic disorders, inflammatory/infectious conditions, tumors, or infiltrative processes. The larger lesion has water density contents and thin, sharp walls, typical of simple cyst. The smaller lesion has nodular walls and higher density contents, suggestive of splenic lymphangioma. Lymphomatous infiltration is also present within the adrenal gland and nodes throughout the abdomen. Note the foci of calcification from histoplasmosis in the main and accessory spleen. A heat-damaged red blood cell scan (not shown) proved this to be an accessory spleen. Masses in the splenic hilum may arise from or involve the tail of the pancreas or spleen. The majority of the small bowel is on one side of the abdomen, in keeping with malrotation. Such large abscesses are unusual in the spleen, especially in the absence of prior splenic infarction. The patient deteriorated rapidly, and multiple tuberculous abscesses were identified at autopsy. This patient had a prior rupture of a hepatic hydatid cyst with diffuse spread throughout the abdomen. Tonolini M et al: Nontraumatic splenic emergencies: cross-sectional imaging pancreatitis findings and triage. Blood cultures identified Staphylococcus and the patient recovered with antibiotics. An echocardiogram showed multiple vegetations in both the aortic and mitral valves, suggesting that this abscess is due to underlying endocarditis. The patient underwent an echocardiogram, which additionally revealed aortic valve vegetations from endocarditis (not shown). The most common causes of massive splenomegaly are cirrhosis/portal hypertension, lymphoma, chronic myelogenous leukemia, extramedullary hematopoiesis, myelofibrosis, and Gaucher disease. In most patients with splenomegaly, there are clues as to the underlying cause on the imaging study, as in this case. Manenti A et al: Splenomegaly Secondary to Myeloproliferative Neoplasms and Portal Hypertension. The patient was later found to have thoracic lymphadenopathy, and biopsy showed the spleen to be a manifestation of sarcoidosis. This normal variant is often more prominent in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. While sickle cell patients can develop a small, calcified autoinfarcted spleen, the spleen may be enlarged in the early stages of the disease. Notice the peripheral enhancement (rim sign) at the margins of the infarct as a result of preserved flow through capsular vessels. Embolic disease is likely the most common cause of splenic infarcts in older patients. Gaetke-Udager K et al: Multimodality imaging of splenic lesions and the role of non-vascular, image-guided intervention. This mass was found at surgery to represent torsion and infarction of a "wandering" spleen. The spleen in such cases is found in ectopic locations due to laxity or absence of the splenic ligaments. This was found at surgery to represent a massively infarcted spleen with contained rupture, resulting in the fluid collection. Massive acute infarction is often not desired in splenic embolotherapy, as patients can develop infections of infarcted tissue. Note the fracture of the lower pole featuring a site of high attenuation arterial extravasation. Splenosis is most commonly seen within the peritoneal cavity, with extraperitoneal splenosis more rare. The patient had a distant history of traumatic splenic injury with diaphragmatic rupture, the most common reason for thoracic splenosis. Note the absence of any enhancing or soft tissue components within this splenic cyst. The patient was symptomatic with pain and early satiety and consequently underwent surgical cyst deroofing. While the typical nodular, centripetal enhancement seen with hepatic hemangiomas is less common in the spleen, splenic hemangiomas often demonstrate avid enhancement. While the mass in the liver superficially resembles a hemangioma, the liver lesion was one of multiple metastases in this patient. Although they resemble hemangiomas with nodular enhancement, these were found to represent metastatic angiosarcoma. The size of the mass raised concern for malignancy and precipitated splenectomy, where the lesion was found to be sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation. The cystic components within the mass are unusual prior to treatment, as lymphoma usually appears as a solid hypodense mass. Diffuse involvement of spleen (or liver) may be difficult to recognize on imaging, often appearing as nonspecific organomegaly. Note the lymphomatous infiltration in the adrenal gland and nodes throughout the abdomen. Melanoma is one of several tumors which can appear cystic, as in this case, and be misinterpreted as a splenic abscess. In most published reports, breast cancer is the most common primary source for splenic metastases.
Cats are the only animal that sheds oocysts in its feces and contaminates the environment with them diabetes insipidus diarrhea generic 25 mg precose with visa. Transmission occurs from environmental contact diabetic vegetables discount precose online, through intermediate hosts diabetic diet glycemic index chart buy discount precose 25 mg on-line, such as birds diabetes mellitus sliding scale cheap precose 25 mg without a prescription, rodents diabetes signs wiki buy genuine precose online, pigs diabetes type 2 clinical trials 25 mg precose sale, sheep, and cattle;. The primary mode of foodborne transmission is ingestion of undercooked or raw meats. In addition, placing hands to mouth after handling cats, their litter box or feces, or anything that may have come in contact with their feces is a source of transmission. Any material that comes in contact with parasite-laced feces is at risk of being contaminated. Target populations Infection is usually asymptomatic, with no obvious symptoms in immunocompetent and otherwise healthy individuals. When symptoms do occur, such as fatigue, flu-like symptoms, muscle aches and pains, and swollen glands, they are usually mild and short-lived. Those most affected are individuals with an impaired immune system and pregnant women. In such cases, illness may be life-threatening, particularly to a developing fetus. Food Analysis Analysis of foods usually is achieved by serology, although tissue cysts may be observed in stained biopsy specimens from infected meats. These include direct contamination of food ingredients or farm-fresh produce; through contaminated water sources used in irrigation, washing, or processing of foods; and through direct human transfer by food handlers or processors or in the home. Epidemiologic evidence suggests that most outbreaks of illness in humans occur through consumption of uncooked or undercooked meat containing viable tissue cysts. Documented outbreaks have been described in which the ingestion of infected meat, such as uncooked pork, was the major source of infection. However, large-scale outbreaks linked to municipal water sources and consumption of unfiltered water have altered such thinking. This includes outbreaks in Canada, in 1994, attributed to a contaminated municipal water supply, and in several regions of Brazil. Bad Bug Book Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Giardia lamblia For Consumers: A Snapshot 1. In some cases, there Giardia intestinalis or Giardia are no symptoms, but, often, people who have duodenalis) is a single-celled, enteric giardiasis (the illness caused by Giardia) have protozoan parasite that moves with the diarrhea that smells especially bad, gas, nausea, aid of five flagella, which also assist cramps, vomiting, and weight loss. People who have with attachment to intestinal giardiasis and who prepare food may contaminate epithelium. The people Giardia is infective in the cyst stage, who eat the food may then get giardiasis. A person when it is also extremely resistant to with poor hygiene can pass Giardia to another environmental stressors, including person through direct contact; for example, if cold temperatures and chemicals. As Giardia gets on the hands, and then into the mouth, noted in the Sources section, below, of the other person. Children in daycare centers chlorine concentrations typically used often get giardiasis in this way. On the farm, for post-harvest rinsing do not kill the contaminated water can contaminate crops. Giardiasis may go away by itself within 2 to 6 weeks Reservoirs for Giardia include the in most people who are otherwise healthy, although intestine of infected humans or other it may last much longer in others. Anyone can get giardiasis, and those at domestic animals (dogs and cats) and higher risk include hikers, hunters, and others who wild animals (beavers, muskrats, might drink water from the outdoors; and children in bears). You can help protect yourself and distinct, organism infects rodents, others from Giardia by washing your hands well although rodents may be infected with after going to the bathroom or cleaning someone human isolates in the laboratory. Outdoor Giardiasis is a very frequent cause of recreation stores sell filters that remove Giardia non-bacterial diarrhea in North from water. America and is one of the most commonly isolated enteric protozoans in clinical specimens. Routes of transmission include contaminated water, food, and person-to-person contact with someone who is ill with giardiasis, especially when adequate fecal-oral hygiene is lacking. However, some (less than 4%) remain symptomatic for more than 2 weeks, possibly leading to a malabsorption syndrome and severe weight loss. Severe dehydration due to loss of fluids is a major concern, especially in young children. Malabsorption of vitamins, protein, and iron all are possible with chronic infections, and it has been suggested that, in children, this can result in stunted growth and development. Chronicity of infection is correlated with an absence of secretory IgA in the intestinal lumen. About 40% of those who are diagnosed with giardiasis develop disaccharide intolerance during infection and up to six months after resolution of infection. Different people infected with the same strain have various degrees of symptoms, and the symptoms of an individual may vary during the course of the disease. Flagyl (metronidazole) is normally quite effective in terminating infections and is the first-line choice. However, treatment lasts for up to 7 days, and substantial side effects are not uncommon. In some patients, it is better tolerated than is flagyl, due to fewer side effects and because treatment is given in a single dose. In some immune-deficient individuals, giardiasis may contribute to a shortening of the life span. When symptoms are present, they generally consist of especially malodorous diarrhea, malaise, abdominal cramps, flatulence, and weight loss. Investigators have been unable to confirm reports that the organism produces a toxin. Infrequently, it has been found in the duodenal cells of its hosts, but this probably is not responsible for the symptoms of the disease. The organism has been found inside host duodenum cells, but this is an infrequent occurrence that is, more than likely, not responsible for disease symptoms. Mechanical obstruction of the absorptive surface of the intestine has been proposed as a possible pathogenic mechanism. The overall incidence of infection in the United States is estimated to be 2% of the population. Giardiasis is more prevalent among children than among adults, possibly because many individuals seem to have a lasting immunity after infection. However, chronic, symptomatic giardiasis is more common in adults than in children. Sources Infection typically results after ingestion of soil, water, or food contaminated with feces of infected humans or animals. However, foodborne outbreaks that were associated with vegetables and lettuce-based salads were reported in 2005 and 2007 and included 65 cases. Infected food handlers are very often implicated in giardiasis outbreaks, suggesting the ease of foodborne transmission. For example, an infected food handler preparing raw vegetables that were later served in an office cafeteria was the probable cause of nearly 30 cases. Giardia cysts are not killed by chlorine levels typically used to rinse produce post-harvest, and are especially difficult to wash off of complex food surfaces like leafy greens and berries. Diagnosis Giardia lamblia is frequently diagnosed by visualizing the organism, either the trophozoite (active reproducing form), or the cyst (the resting stage that is resistant to adverse environmental conditions) in stained preparations or unstained wet mounts of liquid stool, with the aid of a microscope. Commercial direct fluorescence antibody kits are available to stain the organism, with reported sensitivities and specificities reaching 100%. Organisms may be concentrated by sedimentation or flotation; however, these procedures reduce the number of recognizable organisms in the sample. When compared with microscopy, such tests have sensitivities and specificities ranging from 85% to 100%. Target Populations Giardiasis occurs throughout the population, although the prevalence is higher in children than in adults; especially in children 2 to 5 years old, in daycare, where a child-to-child passage rate as high as 50% has been noted. Other high-risk groups include individuals with certain antibody deficiencies and those with decreased gastric acidity. Food Analysis Food is analyzed by thorough surface cleaning of the suspected food and sedimentation of the organisms by centrifugation of wash material. Bad Bug Book Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Entamoeba histolytica For Consumers: A Snapshot 1. All species are characterized by a People who have a weak immune system or take life cycle that alternates between two medicines that lower the actions of the immune distinct stages. The cyst stage is the system (such as some drugs for rheumatoid infectious, but nonreplicative, form of the arthritis or cancer) are more at risk of illness than parasite that will develop in the intestine of are otherwise healthy people. Entamoeba is passed the host into active trophozoites capable of in the bowel movements of infected people and replicating. The cysts can survive symptoms do occur, they range from mild diarrhea freezing and are not always killed by to severe diarrhea that contains mucus and blood, chlorination; however, they do not survive and a swollen abdomen. If it goes to the liver, it can also cause fever, pain, and tenderness in the upper Entamoeba histolytica causes amebiasis (or right part of the abdomen, and nausea. In the United States, cases of Entamoeba histolytica infection are not common, and mortality is likely to be rare. Intestinal amebiasis manifests mostly as asymptomatic colonization, in which the parasite lives within the digestive system, but does not penetrate intestinal cells. In some people, the disease will progress into amoebic colitis after invasion of the intestinal mucosa. On rare occasions (2% to 20% of symptomatic infections), the disease will spread extra intestinally, mostly to the liver, causing amebic liver abscess, or to the brain, spleen, lungs, or genitourinary tract. The severity of the symptoms associated with intestinal amebiasis ranges from mild diarrhea to a severe, dysentery-like illness with mucus and blood in the diarrhea and abdominal distention. Amoebic liver abscess is characterized by fever, pain in the upper right abdomen, nausea, unintentional weight loss, and liver tenderness. Invasion of the intestine will cause symptoms that can last from a few days to several weeks, in the absence of treatment. Both cysts and trophozoites are passed in the feces, but trophozoites do not survive gastric acid. To become invasive, trophozoites secrete toxins that break down the intestinal protective mucus layer, destroy the colonic intestinal barrier, and counter the defense mechanisms of the host. Most infections, morbidity, and mortality occur in South and Central America, Africa, and Asia (Far East and Indian subcontinent). Sources As noted in the Organism section, above, cysts have several characteristics conducive to survival in the environment. Raw foods also may be a source of infection, after contamination by a food handler or by irrigation / rinse water, especially if the food is maintained in a moist environment. People who have chronic amebiasis or are asymptomatic can excrete several million cysts per day. During the acute phase of the illness, people tend to shed more trophozoites than cysts. Light microscopic examination of fecal specimens for cysts and trophozoites does not allow for such differentiation, unless red blood cells are identified inside trophozoites, a strong indication of invasive amebiasis. Biopsy, serology, antigen detection and molecular assays can be used for the specific diagnosis of E. In industrialized countries, this infection is most common among immigrants from endemic areas, travelers to developing nations, and in institutionalized populations. However, the procedure is not very sensitive, as less than 1% of the initial parasitic population may be recovered. Examples of Outbreaks In developed countries, amebic infections tend to cluster in households, in institutions housing people with developmental delayed, or among sexual partners. More recently, an outbreak of amebiasis was reported in the Republic of Georgia, with 177 cases recorded between May 26 and September 3, 1998, including 71 cases of intestinal amebiasis and 106 probable cases of liver abscess. Recent discoveries in the pathogenesis and immune response toward Entamoeba histolytica. Bad Bug Book Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Cryptosporidium parvum 1. The organism is transmitted via of body fluid lost from this illness can be dangerous oocysts. Otherwise healthy people who get this although it is susceptible to drying and illness usually get better in 2 days to 2 weeks. Even anyone who has severe or longerlasting diarrhea, after a 90-minute contact time with seeing a health professional is very important.
Flexible ureterorenoscopy with laser fragmentation has also been used safely and effectively 151 diabetes mellitus news buy cheap precose on-line, 152 with less risk for traumatic nephron loss diabetes insipidus in dogs left untreated proven precose 50mg. Management of renal cyst infection Recent meta-analyses highlight the course and successful management of both renal 153 and liver cyst infections diabetes type 2 inheritance order discount precose line. Blood and urine cultures may be negative and cyst aspiration for culture should be considered if a complex cyst in the right setting is identified diabetes mellitus type 2 signs and symptoms 50 mg precose sale. Lipid-permeable anti-microbial agents such as 28 fluoroquinolones and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole diabetes in dogs sugar levels order genuine precose online, depending on sensitivity (if 158 available) is diabetes in dogs reversible buy discount precose 50 mg on line, remain the standard treatment for cyst infections. Once antibiotic therapy has been initiated, there is wide variability regarding duration of treatment and indications and timing of percutaneous or surgical draining; however extended antibiotic therapy is often warranted. It has a negative impact on sleep, activity, mental status, and social relationships. Health care providers often fail to discuss pain during encounters with patients, leading to suboptimal management. Careful history taking and physical exam (location 160, 161 and characterization of the pain) are the initial steps. Differential diagnosis should be sought by a multidisciplinary workup with radiologists, physical therapists, and pain specialists. Pre-medication therapy needs to be initiated with consultation of the patient and physical therapist. Percutaneous cyst aspiration is helpful as a diagnostic procedure to determine whether a more permanent intervention such as cyst 162, 163 sclerosis or laparoscopic cyst fenestration is worth pursuing. Celiac plexus 164 blockade, radiofrequency ablation, and spinal cord stimulation have also been used. Thoracoscopic sympathosplanchnicectomy may be helpful in some patients with disabling pain but it is invasive and has potential complications such as pneumothorax 165 and orthostatic hypotension. Laparoscopic renal denervation has been helpful in a 166 small series of patients. Counseling for both parents should also discuss the risk of passing on the disease to their offspring, and the risks to both the baby and mother should pregnancy take place. Utilization of appropriate antihypertensive medications documented to be safe in pregnancy is important. Nevertheless, pregnancy induced hypertension and preeclampsia occur more frequently. As for patients with other kidney disease etiologies, a direct comparison of the prognosis of transplanted and non-transplanted patients is difficult, due to strong selection bias. Appropriate individual and family counseling is required to support decision making in such situations. Therefore the indication should be based on a risk-benefit analysis and kidneys should not be routinely removed prior to transplantation. Hand assisted laparoscopic nephrectomy may be better tolerated, although conversion to open nephrectomy may be necessary for very large 186-188 cystic kidneys. Possible indications include recurrent and/or severe infection, symptomatic nephrolithiasis, recurrent and/or severe bleeding, intractable pain, and suspicion of renal cancer. Insufficient space for insertion of a kidney graft may represent an indication for native nephrectomy, but establishing this need is difficult and practices 32 174, 182, 184, 189 vary widely, with pre-transplant nephrectomy rates between 3% and 100%. While no direct comparisons of different strategies are available, on average less than 174, 189, 190 one third of patients in published series undergo pre-transplant nephrectomy, a figure that may serve as a benchmark for transplant programs. The decision for or against nephrectomy should also take into account that native kidney size typically 191 declines after transplantation. Space considerations are usually an indication for unilateral rather than bilateral nephrectomy. Experience with both, prior and 189, 192 simultaneous nephrectomy has been reported but both practices have not been directly compared in a prospective and randomized fashion. Transcatheter artery embolization has been suggested as an alternative to nephrectomy to obtain sufficient 193 volume reduction for graft implantation. However, the optimal donor, organ, and recipient characteristics needed to make this an acceptable strategy have not been defined. In any case, visible hematuria requires evaluation of the entire urinary tract for cause. In general such patients do not appear to be at increased risk for thromboembolic complications. The history of bleeding and/or macrohematuria episodes should influence treatment decisions and trigger work-up in individual patients. Given the safety and accuracy of current imaging methods for screening along with the availability of less invasive treatment modalities, early pre-symptomatic detection is desirable. If screening is negative, should patients be screened again and if so, at what time interval The authors observed that the increased risk did not manifest until approximately 3 years after starting dialysis and they surmised that the risk was mitigated after kidney transplantation. Additional analyses in larger cohorts would be needed to determine whether mutation class could be used reliably for risk stratification. Those individuals who remain anxious about their risk should be offered screening. However, the sudden occurrence of atypical, suddenly intense headache (often described as a thunder clap headache) possibly coupled with other neurologic symptoms, should be considered a neurologic 207 emergency and requires urgent evaluation. Overall endovascular procedures appear to have lower associated morbidity and mortality in comparison with 223, 225, 226 surgical approaches. Nevertheless there remains concern with respect to the durability of coil embolization. However, massive liver enlargement can result in compression of surrounding organs. Compressive symptoms include abdominal pain and distension, back pain, early satiety potentially causing malnutrition, gastroesophageal reflux, compromised lung function with dyspnea or recurrent pneumonia, and hepatic venous 230, 232, 233 outflow obstruction. In one small prospective non-randomized study, polycystic liver volumes 237 increased over one year in post-menopausal women taking estrogens. Progesterone, like estrogens, stimulates the proliferation of cholangiocytes, therefore, contraceptives containing only 238 progestogens may not be safer than those containing estrogens. Aspiration and sclerotherapy involve percutaneous drainage of a cyst with subsequent instillation of an agent such as ethanol that destroys cyst lining cells so that fluid is no longer produced. The main indication for aspiration and sclerotherapy is a large dominant cyst that is causing symptoms. Multiple cysts can be drained at the same time using this procedure, although certain areas of the liver are not amenable to laparoscopic visualization. In one large series (N=124 cases) the perioperative morbidity and mortality 240 were 63% and 3%, respectively. Nonetheless liver resection can provide considerable and sustained symptomatic relief. In the same study, performance status had normalized or improved in ~75% of patients after a mean follow-up of 9 years. Given the complexity and risk of this surgery, partial hepatic resection should only be performed in centers that have extensive experience with this procedure. Many transplant surgeons are reluctant to transplant 40 patients who have previously had liver resection due to the potential for serious complications. Transcatheter arterial embolization of hepatic artery branches that supply major liver 242, 243 cysts has been reported to decrease total liver volume in small series. There is limited experience with this procedure at most centers and therefore larger, controlled studies are needed before this therapy can be recommended. Two long-acting somatostatin analogues, octreotide and lanreotide have been tested in clinical trials and yield a small but reproducible and clinically significant decrement in liver volume over 1-2 years of 135, 136, 244-247 treatment (~ 4% 6%) compared with ~ 0% +1. These agents have been relatively well tolerated, but with side effects including diarrhea, nausea, hyperglycemia and cholelithiasis. Several studies have suggested that most of the benefit is seen over the first year of treatment and that liver cyst volume 245 begins to increase again once the drug is stopped. The response to somatostatin analogues is quite variable but a pooled analysis suggests that women under the age of 248 48 exhibit the most benefit. Clinical features are non-specific and include fever, right 251, 252 upper quadrant tenderness and laboratory data consistent with inflammation. Based on retrospective data, optimal treatment includes drainage of 254 the infected cyst(s) and appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Sampling and culture of infected cyst fluid is important for guiding antimicrobial therapy. The rationale for this approach is that metabolically active inflammatory cells take up high amounts of glucose. Patients with liver cyst infections may require a prolonged course 154 of antibiotics to treat recurrent or persistent infections. In general the choice of an antimicrobial agent will be guided by the culture results but antibiotics that have good 251 cyst penetration such as fluoroquinolones are strongly advised. Aortic insufficiency may be found in association with dilatation of the aortic root. Although these lesions can progress with time, they rarely require valve 2 replacement. In rare circumstances, arachnoid cysts have been 268-270 associated with an increased risk for subdural hematoma. Chronic subdural hematoma may present with headaches and focal neurologic deficits requiring surgical 268 drainage. They rarely present with features of intracranial hypotension (orthostatic headache, diplopia, hearing loss, ataxia) that is caused by cerebrospinal fluid loss. They are usually asymptomatic but cystic compression of the pancreatic duct may rarely cause chronic 273 pancreatitis. Seminal vesicle cysts are rarely symptomatic and we do not recommend routine screening. Therefore, we do not recommend routine screening and imaging should be guided by symptoms. While in these families liver cysts occur in multiple generations, the association with congenital hepatic fibrosis is restricted to single individuals or siblings, suggesting the importance of modifier genes. Upon diagnosis of an index case, siblings should be evaluated for this association. The first diagnosis contact between the patient and physician has major importance. Furthermore, many nephrologists lack time and ability to explain the diagnosis and all its complex implications. There is consensus that all patients need simple, disease-specific information initially, including a printed material that could be read later or at home. Practical implications such as potential impact on work, insurance, lifestyle and family planning should be included. Where possible, patients should be automatically referred to local or national support groups, online references and be encouraged to find someone to talk to . Throughout the consultation, the physician should focus on the possibilities, not the problems, and retain a positive attitude. Physicians should disclose the potential risk for cysts in other organs to provide reassurance and avoid unnecessary investigations. Considerations include ethical, moral, legal, financial, and religious perspectives. Nephrologists and genetic counselors should be objective in their communication of information and options. A patient (and partner when relevant) should feel sufficiently informed and empowered to make their own decisions. For genetic counseling, consistent with current clinical practice, kidney imaging is considered sufficient. With increasing availability of genetic testing and clinical relevance of such 47 17 testing for prognosis, physicians and counselors will need to be trained to communicate the potential benefits and limitations of these analyses. Globally, there is a wide variation in awareness, provision and exclusion of reimbursement of genetic counseling services exists throughout the world. Parents are advised to disclose the diagnosis to a child, strengthen their knowledge and set a good example by including the entire family in a healthy lifestyle program. Physicians should explain the implications of blood test results and offer referral to a renal dietitian as necessary. It is recommended to have some measures of lifestyle change effectiveness studies, in order to encourage patient adherence. Renal dietitians tend to care for patients on dialysis who often follow very strict dietary regimens and the tendency is for negative messages. More comprehensive patient education, with focus on positive messages about diet and lifestyle are required. Where possible, patients could be self-empowered through web-apps and research into these types of patient support programs is encouraged. Exercise is generally recommended, but an individual risk assessment should be carried out for concerns related to enlarged kidneys and/or liver and a disposition to cyst rupture. Many couples split during these difficult times, further increasing stress and poor outcomes. A set of indirect questions for healthcare providers may be developed to circumvent the difficulties inherent in asking such questions. Similarly, a set of prompts for these difficult conversations could also be developed for patients to ask their physicians. Some studies have shown that anxiety is 294 present even in the newly diagnosed, symptomless patients. Diagnosed adults cannot purchase life insurance in many countries and positive diagnosis can impact ability to buy a house in some. Patients should be encouraged to become their own advocates for care and to ask for support and information from their nephrologists.
Purchase precose online from canada. Type 1 vs. Type 2 Diabetes Medical Course.